United Nations Office of Drug and Crime (UNODC): Difference between revisions
JakeDubbert (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Norah.Shamin (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Summary = | |||
UNODC is a global leader in the fight against illicit drugs and international crime. Established in 1997 through a merger between the United Nations Drug Control Programme and the Centre for International Crime Prevention, UNODC operates in all regions of the world through an extensive network of field offices. UNODC relies on voluntary contributions, mainly from Governments, for 90 per cent of its budget. | |||
UNODC is mandated to assist Member States in their struggle against illicit drugs, crime and terrorism. In the Millennium Declaration, Member States also resolved to intensify efforts to fight transnational crime in all its dimensions, to redouble the efforts to implement the commitment to counter the world drug problem and to take concerted action against international terrorism. | |||
This page describes the steps followed to compute the overall drug prevalence rates including and excluding cannabis and to collect the raw data. The first section of the document explains how the UNODC computes drug prevalence rates by country and how these are aggregated. The next sections explain how we compile data from the UNODC, the methodology used to fill holes and the methodology used to derive an aggregate measure of drug prevalence. The next section explains how to collect the raw data.<span style="font-size:larger;"><span style="font-family:times new roman,times,serif;"><ref>http://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/about-unodc/index.html?ref=menutop</ref></span></span> | |||
= Methodology followed by the UNODC = | === Methodology followed by the UNODC === | ||
Drug prevalence is one of the major indicators compiled and used by the UNODC. Data for the same is collected by the UNODC through the use of ARQs (Annual report questionnaires).In cases where prevalence rates are not available for a particular country. The UNODC mentions that the quantity of information provided on illicit drug supply is much better than information provided on drug demand. Where other data is available from different sources, data from the ARQs is supplemented with data from other sources. | |||
A global estimate of the level of use of a specific drug involves the following steps, | |||
* Identification and analysis of appropriate sources | |||
* Identification of key benchmark figures when it comes to measuring drug prevalence (annual prevalence amongst the population 15-64 has been chosen as the key metric) | |||
* Standardization of the existing data if reported with a different reference population | |||
* Imputation of data for countries where no data is available based on the countries in the same sub-region. | |||
* Extrapolation of available results for a sub region are calculated for sub-regions where prevalence rate estimates for at least two countries covering at least 20% of the population are available. If a sub-regional estimate was not extrapolated, a regional calculation was extrapolated based on the 10th and 90th percentile of the distribution of the data available from countries in the region. | |||
* Aggregation of regional estimates rolled-up into regional results to arrive at global estimates. | |||
* When deriving overall prevalence of drug use in any country, total prevalence was calculated and this was divided by 1.12 to account for usage of different drugs by the same individual. | |||
= Table In IFs = | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+ | |||
!Variable | |||
!Definition | |||
!Years | |||
!UsedInPreprocessor | |||
!UsedInPreprocessorFileName | |||
|- | |||
|DrugPrevalenceRateAmphetamines | |||
|Total Drug Prevalence rate for Amphetamines for the population aged 15-64 (unless otherwise specified by the UNODC) compiled using ARQs | |||
|2000-2016 | |||
|1 | |||
|SOCIOPOL | |||
|- | |||
|DrugPrevalenceRateCocaine | |||
|Total Drug Prevalence rate for Cocaine for the population aged 15-64 (unless otherwise specified by the UNODC) compiled using ARQs | |||
|2000-2016 | |||
|1 | |||
|SOCIOPOL | |||
|- | |||
|DrugPrevalenceRateOpiates | |||
|Total Drug Prevalence rate for Opiates for the population aged 15-64 (unless otherwise specified by the UNODC) compiled using ARQs | |||
|2001,2003-2015 | |||
|1 | |||
|SOCIOPOL | |||
|- | |||
|DrugPrevalenceRatePrescriptionOpioids | |||
|Total Drug Prevalence rate for Prescription Opioids for the population aged 15-64 (unless otherwise specified by the UNODC) compiled using ARQs | |||
|2005-2008,2010-2015 | |||
|1 | |||
|SOCIOPOL | |||
|- | |||
|DrugPrevCocaineRegAvg | |||
|Amphetamine use prevalence (Regional averages) | |||
|1998,2001-2016 | |||
|1 | |||
|SOCIOPOL | |||
|- | |||
|DrugPrevAmphetamineRegAvg | |||
|Cocaine use prevalence (Regional averages) | |||
|2002-2021 | |||
|1 | |||
|SOCIOPOL | |||
|- | |||
|DrugPrevOpiateRegAvg | |||
|Opiate use prevalence (Regional averages) | |||
|2002-2021 | |||
|1 | |||
|SOCIOPOL | |||
|- | |||
|DrugPrevPresOpRegAvg | |||
|Prescription opioid use prevalence (Regional averages) | |||
|2001,2003-2021 | |||
|1 | |||
|SOCIOPOL | |||
|- | |||
|DrugPrevalenceRateCannabis | |||
|Total Drug Prevalence rate for Cannabis for the population aged 15-64 (unless otherwise specified by the UNODC) compiled using ARQs | |||
|2003-2021 | |||
|0 | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|DrugPrevalenceRateEcstacy | |||
|Total Drug Prevalence rate for Ecstacy for the population aged 15-64 (unless otherwise specified by the UNODC) compiled using ARQs | |||
|2015,2019-2021 | |||
|0 | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|DrugPrevalenceRateOpioids | |||
|Total Drug Prevalence rate for Opioids for the population aged 15-64 (unless otherwise specified by the UNODC) compiled using ARQs | |||
|2015,2019-2021 | |||
|0 | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|DrugPrevalenceRatePrescription Stimulants | |||
|Total Drug Prevalence rate for Prescription Stimulants for the population aged 15-64 (unless otherwise specified by the UNODC) compiled using ARQs | |||
|2015,2019-2021 | |||
|0 | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|DrugPrevalenceRateTranquilizersandSedatives | |||
|Total Drug Prevalence rate for Tranquilizers and Sedatives for the population aged 15-64 (unless otherwise specified by the UNODC) compiled using ARQs | |||
|2015,2019-2021 | |||
|0 | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|CrimesDrugper100000 | |||
|Total Drug-Related Crimes at the national level, number of police-recorded offences, per 100000 | |||
|2003-2008 | |||
|0 | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|CrimesHomicper100000 | |||
|Intentional homicide, rate per 100000 | |||
|1995-2010 | |||
|0 | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|CrimesPrisonersper100000 | |||
|Total sentenced persons held, rate per 100000 | |||
|2003-2009 | |||
|0 | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|CrimesKidnapping | |||
|Drug Possession/Use at the national level, number of police-recorded offences , rate per 100000 | |||
|2003-2009 | |||
|0 | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|CrimesAssault | |||
|Assault at the national level, number of police-recorded offences, rate per 100000 | |||
|2003-2009 | |||
|0 | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|CrimesProperty | |||
|Theft at the national level, number of police-recorded offences, per 100000 | |||
|2003-2009 | |||
|0 | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|CrimesRobbery | |||
|Robbery at the national level, number of police-recorded offences, rate per 100000 | |||
|2003-2009 | |||
|0 | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
|CrimesSexualAssault | |||
|Rape at the national level, number of police-recorded offences, rate per 100000 | |||
|2003-2009 | |||
|0 | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
= Data Pulling Instructions = | |||
Step 1: Navigate to the [https://dataunodc.un.org/ Data UNODC Home Page] [[File:UNODC Main Page.png|none|thumb|800x800px]] | |||
Step 2: Click the "Drug Use & Treatment". | |||
Step 3: Choose which data you need:[[File:UNODC Home Page.png|none|thumb|800x800px]]Step 4: I will use "Prevalence of drug use" as an example. Click "Dataset" in the top right corner. | |||
<span style="font-size:larger;"><span style="font-family:times new roman,times,serif;"> | Step 5: You will be navigated to the [https://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/data-and-analysis/wdr2023_annex.html drug report page].[[File:Statistical Annex.png|none|thumb|800x800px]]Once you click on a link, it will automatically download the excel sheet. Then you can pull the data you need. See Data Notes for more detailed instructions. <div> | ||
= Data Notes = | |||
# '''1.1 Prevalence of drug use in the general population - regional and global estimates''' was downloaded for series with "RegAvg". Dataset is only in the most recent 1 year. | |||
# '''1.2 Prevalence of drug use in the general population, including NPS - national data''' was downloaded for series with "PrevalenceRate"<span style="font-size:larger;"><span style="font-family:times new roman,times,serif;">.</span></span> | |||
# Always filter the dataset "Age" to "15-64". | |||
# For series with "RegAvg", assign the countries to the regions based on the "Regional Mapping" (Next to "Dataset" in photo in step 3). | |||
#* Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic was assigned to North Africa. | |||
# For series with "RegAvg", datasets from 2019 - 2020 can be found below, download the data with similar name in Note 1. | |||
#* 2020: <nowiki>https://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/data-and-analysis/wdr2022_annex.html</nowiki> | |||
#* 2019: <nowiki>https://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/data-and-analysis/wdr2021_annex.html</nowiki> | |||
# Special Country Concordance: | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|Country/Territory | |||
|Country | |||
|FIPS_CODE | |||
|- | |||
|United Kingdom (England and Wales) | |||
|United Kingdom | |||
|GBR | |||
|- | |||
|United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) | |||
|United Kingdom | |||
|GBR | |||
|- | |||
|United Kingdom (Scotland) | |||
|United Kingdom | |||
|GBR | |||
|- | |||
|Turkiye | |||
|Turkey | |||
|TUR | |||
|} | |||
== Data Notes: Drug Prevalence Rate == | |||
For the purpose of computing total prevalence rates we used drug prevalence datasets from the UNODC. These datasets can be found here- <nowiki>https://data.unodc.org/</nowiki>. We computed two main measures, total drug prevalence rate including cannabis and total drug prevalence rate excluding cannabis. Prevalence rates were computed for each drug type namely, | |||
* Amphetamines | |||
* Cannabis | |||
* Cocaine | |||
* Ecstasy | |||
* Opiates | |||
* Opioids | |||
* Prescription Opioids | |||
* Tranquilizers and sedatives | |||
To make all of these drug datasets comparable, holes were filled for country years using | |||
* Interpolation and extrapolation, where holes had to be filled for countries with data for some years | |||
* Sub-regional averages at the sub-region year value were used to fill holes where no data was available for country years | |||
* Regional averages were used to fill holes where sub-regional averages were not available. | |||
One important point to note is that no hole filling was done where the UNODC did not report prevalence rates for a particular country for any drug. For example, the UNODC did not report data for any drug for Angola, therefore no data was filled in for the country using the steps described above. | |||
Finally, when deriving the total prevalence rate, the average prevalence rate was divided by 1.12 to account for usage of multiple drugs by the same user. As mentioned earlier, this is in line with the methodology used by the UNODC.<div> | |||
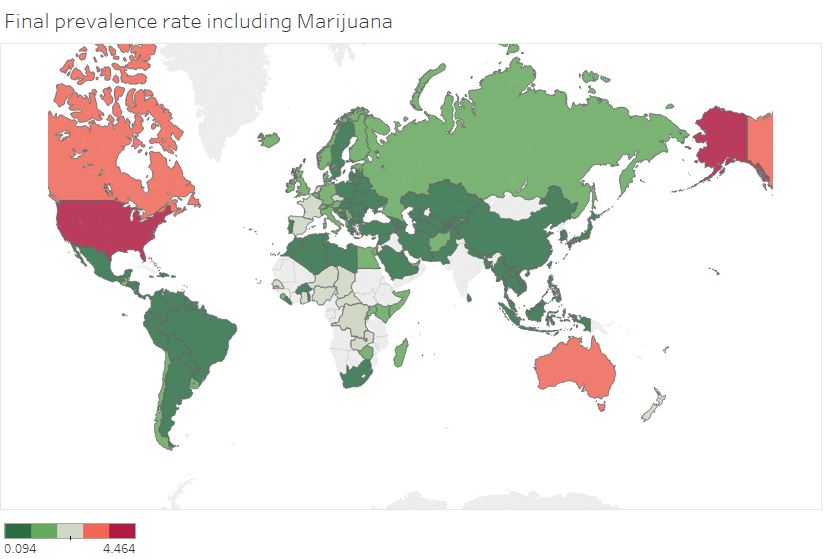
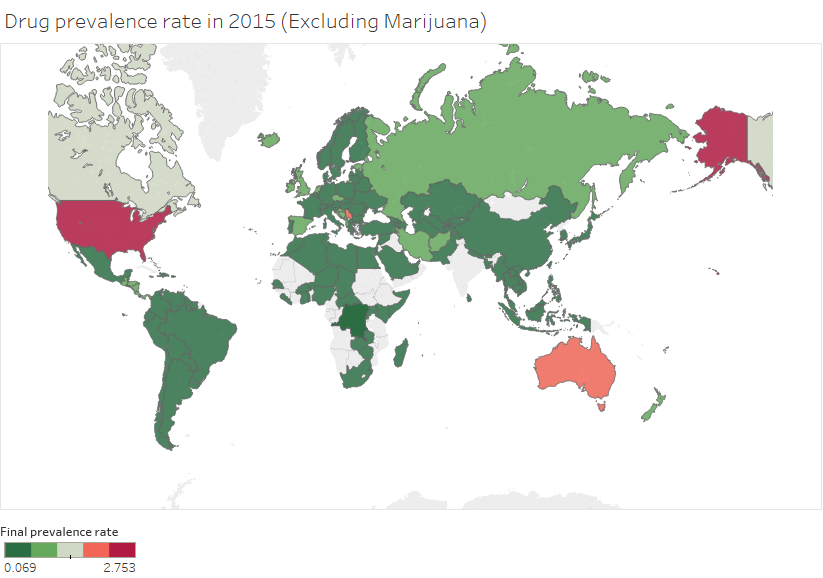
=== Sample Results === | |||
[[File:UNODC Pic 2.png|frame|none|500x300px|Figure 1 : Total prevalence rate including cannabis across countries in 2015]] [[File:UNODC Pic 1.png|frame|none|500x300px|Figure 2: Total drug prevalence rate excluding cannabis in 2015 across countries]]</div> | |||
= References = | = References = | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:00, 4 September 2025
Summary
UNODC is a global leader in the fight against illicit drugs and international crime. Established in 1997 through a merger between the United Nations Drug Control Programme and the Centre for International Crime Prevention, UNODC operates in all regions of the world through an extensive network of field offices. UNODC relies on voluntary contributions, mainly from Governments, for 90 per cent of its budget.
UNODC is mandated to assist Member States in their struggle against illicit drugs, crime and terrorism. In the Millennium Declaration, Member States also resolved to intensify efforts to fight transnational crime in all its dimensions, to redouble the efforts to implement the commitment to counter the world drug problem and to take concerted action against international terrorism.
This page describes the steps followed to compute the overall drug prevalence rates including and excluding cannabis and to collect the raw data. The first section of the document explains how the UNODC computes drug prevalence rates by country and how these are aggregated. The next sections explain how we compile data from the UNODC, the methodology used to fill holes and the methodology used to derive an aggregate measure of drug prevalence. The next section explains how to collect the raw data.[1]
Methodology followed by the UNODC
Drug prevalence is one of the major indicators compiled and used by the UNODC. Data for the same is collected by the UNODC through the use of ARQs (Annual report questionnaires).In cases where prevalence rates are not available for a particular country. The UNODC mentions that the quantity of information provided on illicit drug supply is much better than information provided on drug demand. Where other data is available from different sources, data from the ARQs is supplemented with data from other sources.
A global estimate of the level of use of a specific drug involves the following steps,
- Identification and analysis of appropriate sources
- Identification of key benchmark figures when it comes to measuring drug prevalence (annual prevalence amongst the population 15-64 has been chosen as the key metric)
- Standardization of the existing data if reported with a different reference population
- Imputation of data for countries where no data is available based on the countries in the same sub-region.
- Extrapolation of available results for a sub region are calculated for sub-regions where prevalence rate estimates for at least two countries covering at least 20% of the population are available. If a sub-regional estimate was not extrapolated, a regional calculation was extrapolated based on the 10th and 90th percentile of the distribution of the data available from countries in the region.
- Aggregation of regional estimates rolled-up into regional results to arrive at global estimates.
- When deriving overall prevalence of drug use in any country, total prevalence was calculated and this was divided by 1.12 to account for usage of different drugs by the same individual.
Table In IFs
| Variable | Definition | Years | UsedInPreprocessor | UsedInPreprocessorFileName |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DrugPrevalenceRateAmphetamines | Total Drug Prevalence rate for Amphetamines for the population aged 15-64 (unless otherwise specified by the UNODC) compiled using ARQs | 2000-2016 | 1 | SOCIOPOL |
| DrugPrevalenceRateCocaine | Total Drug Prevalence rate for Cocaine for the population aged 15-64 (unless otherwise specified by the UNODC) compiled using ARQs | 2000-2016 | 1 | SOCIOPOL |
| DrugPrevalenceRateOpiates | Total Drug Prevalence rate for Opiates for the population aged 15-64 (unless otherwise specified by the UNODC) compiled using ARQs | 2001,2003-2015 | 1 | SOCIOPOL |
| DrugPrevalenceRatePrescriptionOpioids | Total Drug Prevalence rate for Prescription Opioids for the population aged 15-64 (unless otherwise specified by the UNODC) compiled using ARQs | 2005-2008,2010-2015 | 1 | SOCIOPOL |
| DrugPrevCocaineRegAvg | Amphetamine use prevalence (Regional averages) | 1998,2001-2016 | 1 | SOCIOPOL |
| DrugPrevAmphetamineRegAvg | Cocaine use prevalence (Regional averages) | 2002-2021 | 1 | SOCIOPOL |
| DrugPrevOpiateRegAvg | Opiate use prevalence (Regional averages) | 2002-2021 | 1 | SOCIOPOL |
| DrugPrevPresOpRegAvg | Prescription opioid use prevalence (Regional averages) | 2001,2003-2021 | 1 | SOCIOPOL |
| DrugPrevalenceRateCannabis | Total Drug Prevalence rate for Cannabis for the population aged 15-64 (unless otherwise specified by the UNODC) compiled using ARQs | 2003-2021 | 0 | |
| DrugPrevalenceRateEcstacy | Total Drug Prevalence rate for Ecstacy for the population aged 15-64 (unless otherwise specified by the UNODC) compiled using ARQs | 2015,2019-2021 | 0 | |
| DrugPrevalenceRateOpioids | Total Drug Prevalence rate for Opioids for the population aged 15-64 (unless otherwise specified by the UNODC) compiled using ARQs | 2015,2019-2021 | 0 | |
| DrugPrevalenceRatePrescription Stimulants | Total Drug Prevalence rate for Prescription Stimulants for the population aged 15-64 (unless otherwise specified by the UNODC) compiled using ARQs | 2015,2019-2021 | 0 | |
| DrugPrevalenceRateTranquilizersandSedatives | Total Drug Prevalence rate for Tranquilizers and Sedatives for the population aged 15-64 (unless otherwise specified by the UNODC) compiled using ARQs | 2015,2019-2021 | 0 | |
| CrimesDrugper100000 | Total Drug-Related Crimes at the national level, number of police-recorded offences, per 100000 | 2003-2008 | 0 | |
| CrimesHomicper100000 | Intentional homicide, rate per 100000 | 1995-2010 | 0 | |
| CrimesPrisonersper100000 | Total sentenced persons held, rate per 100000 | 2003-2009 | 0 | |
| CrimesKidnapping | Drug Possession/Use at the national level, number of police-recorded offences , rate per 100000 | 2003-2009 | 0 | |
| CrimesAssault | Assault at the national level, number of police-recorded offences, rate per 100000 | 2003-2009 | 0 | |
| CrimesProperty | Theft at the national level, number of police-recorded offences, per 100000 | 2003-2009 | 0 | |
| CrimesRobbery | Robbery at the national level, number of police-recorded offences, rate per 100000 | 2003-2009 | 0 | |
| CrimesSexualAssault | Rape at the national level, number of police-recorded offences, rate per 100000 | 2003-2009 | 0 |
Data Pulling Instructions
Step 1: Navigate to the Data UNODC Home Page
Step 2: Click the "Drug Use & Treatment".
Step 3: Choose which data you need:

Step 4: I will use "Prevalence of drug use" as an example. Click "Dataset" in the top right corner. Step 5: You will be navigated to the drug report page.
Once you click on a link, it will automatically download the excel sheet. Then you can pull the data you need. See Data Notes for more detailed instructions.
Data Notes
- 1.1 Prevalence of drug use in the general population - regional and global estimates was downloaded for series with "RegAvg". Dataset is only in the most recent 1 year.
- 1.2 Prevalence of drug use in the general population, including NPS - national data was downloaded for series with "PrevalenceRate".
- Always filter the dataset "Age" to "15-64".
- For series with "RegAvg", assign the countries to the regions based on the "Regional Mapping" (Next to "Dataset" in photo in step 3).
- Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic was assigned to North Africa.
- For series with "RegAvg", datasets from 2019 - 2020 can be found below, download the data with similar name in Note 1.
- 2020: https://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/data-and-analysis/wdr2022_annex.html
- 2019: https://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/data-and-analysis/wdr2021_annex.html
- Special Country Concordance:
| Country/Territory | Country | FIPS_CODE |
| United Kingdom (England and Wales) | United Kingdom | GBR |
| United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) | United Kingdom | GBR |
| United Kingdom (Scotland) | United Kingdom | GBR |
| Turkiye | Turkey | TUR |
Data Notes: Drug Prevalence Rate
For the purpose of computing total prevalence rates we used drug prevalence datasets from the UNODC. These datasets can be found here- https://data.unodc.org/. We computed two main measures, total drug prevalence rate including cannabis and total drug prevalence rate excluding cannabis. Prevalence rates were computed for each drug type namely,
- Amphetamines
- Cannabis
- Cocaine
- Ecstasy
- Opiates
- Opioids
- Prescription Opioids
- Tranquilizers and sedatives
To make all of these drug datasets comparable, holes were filled for country years using
- Interpolation and extrapolation, where holes had to be filled for countries with data for some years
- Sub-regional averages at the sub-region year value were used to fill holes where no data was available for country years
- Regional averages were used to fill holes where sub-regional averages were not available.
One important point to note is that no hole filling was done where the UNODC did not report prevalence rates for a particular country for any drug. For example, the UNODC did not report data for any drug for Angola, therefore no data was filled in for the country using the steps described above.
Finally, when deriving the total prevalence rate, the average prevalence rate was divided by 1.12 to account for usage of multiple drugs by the same user. As mentioned earlier, this is in line with the methodology used by the UNODC.Sample Results