|
|
| (24 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| = <span style="font-size:xx-large;">Purposes</span> = | | = <span style="font-size:xx-large;">Purposes</span> = |
|
| |
|
| '''International Futures (IFs) is a tool for thinking about long-term global trends and planning more strategically for the future. ''' | | '''The International Futures (IFs) model helps us explore, understand, and shape global questions about future human well-being. The model empowers users to examine past trends to understand the current trajectory we are on, how human, social, and environmental systems interact over time, and how we think about and address the complex challenges awaiting the global community.''' |
|
| |
|
| IFs can help you: | | '''IFs can help you:''' |
|
| |
|
| *Understand the state of major global systems | | *understand the state of major global systems. |
| *Explore long-term trends and consider where they might take us | | *explore long-term trends and consider where they might take us. |
| *Learn about the dynamic interactions between global systems | | *learn about the dynamic interactions between global systems. |
| *Clarify long-term organizational goals/priorities | | *clarify long-term organizational goals and priorities. |
| *Develop alternative scenarios (if-then statements) about the future | | *develop alternative scenarios (if-then statements) about the future. |
| *Investigate how different groups (households, firms or governments) can shape the future | | *investigate how different groups (households, firms or governments) can shape the future. |
| | *evaluate the potential impacts of policies. |
|
| |
|
| '''IFs development and analysis depend on core, underlying assumptions, including the following.''' | | '''The IFs platform relies on core, underlying assumptions, including the following.''' |
|
| |
|
| *Global issues are becoming more significant as the scope of human interaction and human impact on the broader environment grow. | | *Global issues are becoming more significant as the scope of human interaction and human impact on the broader environment grow. |
| Line 19: |
Line 20: |
| *The domain of human choice and action is broadening. | | *The domain of human choice and action is broadening. |
|
| |
|
| '''What issues can you investigate with IFs?''' | | '''Which issues can you investigate with IFs? Some examples grouped by issue area include:''' |
|
| |
|
| *[[Environment]]: Atmospheric carbon dioxide levels, world forest area, fossil fuel usage | | *[[Environment]]: Atmospheric carbon dioxide levels, world forest area, and temperature change |
| *[[Socio-Political|Socio-Political Change]]: Life expectancy, literacy rate, democracy level, status of women, value change | | *[[Infrastructure]]: Electricity access, and number of fixed broadband subscriptions |
| *[[Population|Demographics]]: Population levels and growth, fertility, mortality, migration | | *[[Health]]: Life expectancy, HIV prevalence, and death rates by category of cause |
| *[[Agriculture|Food and Agriculture]]: Land use and production levels, calorie availability, malnutrition rates | | *[[Education]]: Average years of education, and literacy rate |
| *[[Energy]]: Resource and production levels, demand patterns, renewable energy share | | *[[Governance]]: Democracy level, expenditure and spending levels, and debt level |
| *[[Economics]]: Sectoral production, consumption, and trade patterns and structural change | | *Human Development: Poverty level, and status of women |
| *[[Interstate_Politics_(IP)|Geopolitics]]: Country and regional power levels
| | *[[Interstate Politics (IP)|International Relations]]: Country and regional power levels, and interstate conflict likelihood |
| | *[[Population|Demographics]]: Population levels and growth, fertility, mortality, and migration |
| | *[[Agriculture]]: Land use and production levels, calorie availability, and malnutrition rates |
| | *[[Energy]]: Resource and production levels, demand patterns, fossil fuel usage, and renewable energy share |
| | *[[Economics]]: Sectoral production, consumption, trade patterns, and structural change |
|
| |
|
| = <span style="font-size:xx-large;">IFs Issues and Modules: Visual Representation</span> = | | = <span style="font-size:xx-large;">IFs Issues and Modules: Visual Representation</span> = |
| Line 35: |
Line 40: |
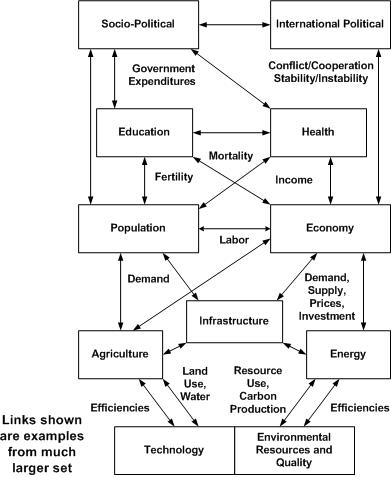
| Among the philosophical premises of the International Futures (IFs) project is that the model cannot be a "black box" to users and be truly useful. Model users must be able to examine the structures of IFs in order (1) to have confidence in them, and (2) learn from them. | | Among the philosophical premises of the International Futures (IFs) project is that the model cannot be a "black box" to users and be truly useful. Model users must be able to examine the structures of IFs in order (1) to have confidence in them, and (2) learn from them. |
|
| |
|
| There is available (see topics under Understanding the Mode in the contents of this help system):
| | The following topics are useful starting points for better understanding the model. |
|
| |
|
| *[[Understand_IFs#Dominant_Relations|Dominant Relations]] of the model structure | | *[[Understand_IFs#Dominant_Relations|Dominant Relations]] of the model structure |
| *[[Understand_IFs#2.2|Structure-Based and Agent-Class Driven Modeling]] | | *[[Understand_IFs#2.2|Structure-Based and Agent-Class Driven Modeling]] |
| *[[Understand_IFs#Equation_Notation|Equation Notation]] | | *[[Understand_IFs#Equation_Notation|Equation Notation]] |
| *[[Introduction_to_IFs#IFs_Bibliography|IFs Bibliography]] of data and data sources | | *[[IFs_Bibliography|IFs Bibliography]] of data and data sources |
|
| |
|
| = <span style="font-size:xx-large;">IFs Issues and Modules: Quick Survey</span> = | | = <span style="font-size:xx-large;">IFs Issues and Models: Quick Survey</span> = |
|
| |
|
| The '''population''' module:
| | International Futures is a collection of interconnected models (sometimes referred to as modules). Below is a quick survey of the major models in IFs. For more information on each one, please click on the model headings. |
|
| |
|
| *represents 22 age-sex cohorts to age 100+
| | The [[Population|demographics]] model: |
| *calculates change in fertility and mortality rates in response to income, income distribution, and analysis multipliers
| |
| *computes average life expectancy at birth, literacy rate, and overall measures of human development (HDI) and physical quality of life
| |
| *represents migration and HIV/AIDS
| |
| *includes a newly developing submodel of formal education across primary, secondary, and tertiary levels
| |
|
| |
|
| The '''economic''' module:
| | *represents 22 age-sex cohorts to age 100+. |
| | *calculates change in fertility and mortality rates in response to income, income distribution, and analysis multipliers. |
| | *computes average life expectancy at birth and represents migration. |
|
| |
|
| *represents the economy in six sectors: agriculture, materials, energy, industry, services, and ICT (other sectors could be configured, using raw data from the GTAP project)
| | The [[Economics|economic]] model: |
| *computes and uses input-output matrices that change dynamically with development level
| |
| *is a general equilibrium-seeking model that does not assume exact equilibrium will exist in any given year; rather it uses inventories as buffer stocks and to provide price signals so that the model chases equilibrium over time
| |
| *contains an endogenous production function that represents contributions to growth in multifactor productivity from R&D, education, worker health, economic policies ("freedom"), and energy prices (the "quality" of capital)
| |
| *uses a Linear Expenditure System to represent changing consumption patterns
| |
| *utilizes a "pooled" rather than the bilateral trade approach for international trade
| |
| *is being imbedded during 2002 in a social accounting matrix (SAM) envelope that will tie economic production and consumption to intra-actor financial flows
| |
|
| |
|
| The '''agricultural''' module:
| | *represents the economy in six sectors: agriculture, raw materials, energy, manufactures, services, and ICT (other sectors could be configured, using raw data from the GTAP project). |
| | *is a general equilibrium-seeking model that does not assume exact equilibrium will exist in any given year; rather it uses inventories as buffer stocks and to provide price signals so that the model chases equilibrium over time. |
| | *contains an endogenous production function that represents contributions to growth in multifactor productivity from R&D, education, worker health, economic policies ("freedom"), and energy prices (the "quality" of capital). |
| | *uses multifactor productivity from the production function along with labor and capital stock as the main drivers of the magnitude of production. |
| | *utilizes a "pooled" rather than the bilateral trade approach for international trade. |
| | *computes and uses a social accounting matrix (SAM) that ties economic production and consumption to intra-actor financial flows both domestically and internationally for households, governments, and industry. |
| | *uses the SAM to calculate changes in income distributions based on its projection of household consumption and on the education model's projections of skill level. |
|
| |
|
| *represents production, consumption and trade of crops and meat; it also carries ocean fish catch and aquaculture in less detail
| | The [[Agriculture|agricultural]] model: |
| *maintains land use in crop, grazing, forest, urban, and "other" categories
| |
| *represents demand for food, for livestock feed, and for industrial use of agricultural products
| |
| *is a partial equilibrium model in which food stocks buffer imbalances between production and consumption and determine price changes
| |
| *overrides the agricultural sector in the economic module unless the user chooses otherwise
| |
|
| |
|
| The '''energy''' module:
| | *represents production, consumption and trade of crops, meat, and fish. |
| | *maintains land use in crop, grazing, forest, urban, and "other" categories; and water use. |
| | *represents demand for food, for livestock feed, and for industrial use of agricultural products. |
| | *is a partial equilibrium model in which food stocks buffer imbalances between production and consumption and determine price changes. |
| | *overrides the agricultural sector in the economic module unless the user chooses otherwise. |
|
| |
|
| *portrays production of six energy types: oil, gas, coal, nuclear, hydroelectric, and other renewable
| | The [[energy]] model: |
| *represents consumption and trade of energy in the aggregate
| |
| *represents known reserves and ultimate resources of the fossil fuels
| |
| *portrays changing capital costs of each energy type with technological change as well as with draw-downs of resources
| |
| *is a partial equilibrium model in which energy stocks buffer imbalances between production and consumption and determine price changes
| |
| *overrides the energy sector in the economic module unless the user chooses otherwise
| |
|
| |
|
| The two '''socio-political''' sub-modules:
| | *portrays production of six energy types: oil, natural gas, coal, nuclear, hydroelectric, and other renewable. |
| | *represents consumption and trade of energy in the aggregate. |
| | *represents known reserves and ultimate resources of fossil fuels. |
| | *portrays changing capital costs of each energy type with technological change as well as with drawdowns of resources. |
| | *is a partial equilibrium model in which energy stocks buffer imbalances between production and consumption and determine price changes. |
| | *overrides the energy sector in the economic module unless the user chooses otherwise. |
|
| |
|
| Within countries or geographic groupings
| | The [[Interstate Politics (IP)|international relations]] model: |
|
| |
|
| *represents fiscal policy through taxing and spending decisions
| | *represents the prospects for state instability or failure. |
| *shows six categories of government spending: military, health, education, R&D, foreign aid, and a residual category
| |
| *represents changes in social conditions of individuals (like fertility rates or literacy levels), attitudes of individuals (such as the level of materialism/postmaterialism of a society from the World Value Survey), and the social organization of people (such as the status of women)
| |
| *represents the evolution of democracy
| |
| *represents the prospects for state instability or failure | |
|
| |
|
| Between countries or groupings of countries
| | *traces changes in power balances across states and regions. |
| | *allows exploration of changes in the level of interstate threat. |
| | *represents possible action-reaction processes and arms races with associated potential for conflict among countries. |
| | The [[governance]] model: |
|
| |
|
| *traces changes in power balances across states and regions | | *is a two-way interaction between governments and the socio-cultural system. |
| *allows exploration of changes in the level of interstate threat | | *has three dimensions of governance: capacity, security, and inclusion that closely interact bi-directionally. |
| *represents possible action-reaction processes and arms races with associated potential for conflict among countries | | *represents the evolution of democracy. |
| | *represents fiscal policy through taxing and spending decisions. |
| | *shows six categories of government spending: military, health, education, R&D, foreign aid, and a residual category. |
|
| |
|
| The implicit '''environmental''' module: | | The [[infrastructure]] model: |
|
| |
|
| *is distributed throughout the overall model | | * forecasts the demand for infrastructure and the funding available to meet the demand. |
| *allows tracking of remaining resources of fossil fuels, of the area of forested land, of water usage, and of atmospheric carbon dioxide emissions | | * forecasts levels of infrastructure based on this demand and funding constraint. |
| | * measures access to key infrastructures like water, electricity, or broadband. |
| | * maintains and calculates changes in physical stocks like percentage of roads paved, and area equipped with irrigation. |
|
| |
|
| The implicit '''technology''' module: | | The [[health]] model: |
|
| |
|
| *is distributed throughout the overall model | | * forecasts age, sex, and health indicators related to 15 causes of death modeled in IFs. |
| *allows changes in assumptions about rates of technological advance in agriculture, energy, and the broader economy
| | * splits the causes of death into three cause groups: communicable, maternal, perinatal, and nutritional conditions; noncommunicable diseases; and injuries. |
| *explicitly represents the extent of electronic networking of individuals in societies | | * is driven by education, technology, and income. |
| *is tied to the governmental spending model with respect to R&D spending | |
|
| |
|
| = <span style="font-size:xx-large;">IFs Background</span> =
| | The [[education]] model: |
|
| |
|
| International Futures (IFs) has evolved since 1980 through three "generations," with a fourth generation now taking form.
| | * projects educational participation and attainment across primary, secondary, and tertiary levels for each country in IFs. |
| | * determines attainment and participation through the demand for education and the investment in education by governments. |
| | * has educational demand based on income while educational investment is a result of government spending. |
| | * models the rates of dropout, completion, and transition to the next level of schooling. |
|
| |
|
| The first generation had deep roots in the world models of the 1970s, including those of the Club of Rome. In particular, IFs drew on the Mesarovic-Pestel or World Integrated Model (Mesarovic and Pestel 1974). The author of IFs had contributed to that project, including the construction of the energy submodel. IFs consciously also drew on the Leontief World Model (Leontief et al. 1977), the Bariloche Foundation’s world model (Herrera et al. 1976), and Systems Analysis Research Unit Model (SARU 1977), following comparative analysis of those models by Hughes (1980). That generation was written in FORTRAN and available for use on main-frame computers through CONDUIT, an educational software distribution center at the University of Iowa. Although the primary use of that and subsequent generations was by students, IFs has always had some policy analysis capability that has appealed to specialists. For example, the U.S. Foreign Service Institute used the first generation of IFs in a mid-career training program. | | The [[Environment|environmental]] model: |
| | *is distributed throughout the overall model. |
| | *allows tracking of remaining resources of fossil fuels, of the area of forested land, of water usage, and of atmospheric carbon dioxide emissions. |
|
| |
|
| The second generation of International Futures moved to early microcomputers in 1985, using the DOS platform. It was a very simplified version of the original IFs without regional or country differentiation. | | The implicit technology model: |
|
| |
|
| The third generation, first available in 1993, became a full-scale microcomputer model. The third generation improved earlier representations of demographic, energy, and food systems, but added new environmental and socio-political content. It built upon the collaboration of the author with the GLOBUS project, and it adopted the economic submodel of GLOBUS (developed by the author). GLOBUS had been created with the inspiration of Karl Deutsch and under the leadership of Stuart Bremer (1987) at the Wissenschaftszentrum in Berlin.
| | *is distributed throughout the overall model. |
| | *allows changes in assumptions about rates of technological advance in agriculture, energy, and the broader economy. |
| | *explicitly represents the extent of electronic networking of individuals in societies. |
| | *is tied to the governmental spending model with respect to R&D spending. |
| | *represents changes in social conditions of individuals (like fertility rates or literacy levels), attitudes of individuals (such as the level of materialism/post-materialism of a society from the World Value Survey), and the social organization of people (such as the status of women). |
|
| |
|
| The third generation has produced three editions/major releases of IFs, each accompanied by a book also called International Futures (Hughes 1993, 1996, 1999). The second edition moved to a Visual Basic platform that allowed a much improved menu-driven interface, running under Windows. The third edition incorporated an early global mapping capability and an initial ability to do cross-sectional and longitudinal data analysis.
| | = <span style="font-size:xx-large;">IFs Background</span> = |
|
| |
|
| The fourth generation has been taking shape since early 2000. It has been heavily influenced by the usage of the model in an increasingly policy-analysis mode by several important organizations. First, General Motors commissioned a specialized version of IFs named CoVaTrA (Consumer Values Trends Analysis) with a need for updated and extended demographic modeling and representation of value change. An alliance was established with the World Values Survey, directed by Ronald Inglehart, to create that version. Second, the Strategic Assessments Group of the Central Intelligence Agency commissioned a specialized version named IFs for SAG. The work involved in preparing that greatly extended and enhanced the socio-political representations of the model, both domestic and international. Third, the European Commission sponsored a project named TERRA which has led to a specialized version named IFs for TERRA. IFs for TERRA work led to enhancements across the model, including improved representation of economic sectors, updated IO matrices and a basic Social Accounting Matrix, GINI and Lorenz curves, and preparing for extended environmental impact representation (drawing upon the Advanced Sustainability Analysis framework of the Finland Futures Research Center).
| | International Futures (IFs) has evolved since 1980 through eight "generations," with the eighth generation now taking form. |
|
| |
|
| Throughout this emergence of a fourth generation IFs (incorporating all of the above elements for additional users) there has been also a heavy emphasis on enhanced usability. Ideas from Robert Pestel in the TERRA project led to the creation of a new tree-structure for scenario creation and management. Ideas from Ronald Inglehart led to the development of the Guided Use structure and a somewhat more game-like character within that structure. Inglehart also help arrange funding to support the programming of Guided Use through the European Union Center of the University of Michigan.
| | '''The first generation''' had deep roots in the world models of the 1970s, including those of the Club of Rome. In particular, IFs drew on the Mesarovic-Pestel or World Integrated Model (Mesarovic and Pestel 1974). The author of IFs had contributed to that project, including the construction of the energy submodule. IFs consciously also drew on the Leontief World Model (Leontief et al. 1977), the Bariloche Foundation’s world model (Herrera et al. 1976), and Systems Analysis Research Unit Model (SARU 1977), following comparative analysis of those models by Hughes (1980). That generation was written in FORTRAN and available for use on main-frame computers through CONDUIT, an educational software distribution center at the University of Iowa. Although the primary use of that and subsequent generations was by students, IFs has always had some policy analysis capability that has appealed to specialists. For example, the U.S. Foreign Service Institute used the first generation of IFs in a mid-career training program. |
|
| |
|
| The fifth version of IFs is currently in use and represents broad strides to improving the model and its usability. It is the first version of this software to be placed online due to the help of the National Intelligence Council ([http://www.ifs.du.edu http://www.ifs.du.edu]). Also, usability has been increased as Packaged Displays and Flex Packaged Displays were introduced that allowed for the creation of very specific lists of countries/regions, groups or Glists. A new education model has also been incorporated into the broader IFs model. New scenarios were created for UNEP (focusing on environmental change) and Pardee (focusing on poverty). Finally, one of the largest changes made was incorporating 182 countries into the Base-Case scenario used by IFs. Previous versions of IFs used broader regions to forecast global trends. This change also did away with the Student and Professional versions. | | '''The second generation''' of International Futures moved to early microcomputers in 1985, using the DOS platform. It was a very simplified version of the original IFs without regional or country differentiation. |
|
| |
|
| = <span style="font-size:xx-large;">Geographic Representation of the World</span> =
| | '''The third generation''', first available in 1993, became a full-scale microcomputer model. The third generation improved earlier representations of demographic, energy, and food systems, but added new environmental and socio-political content. It built upon the collaboration of the author with the GLOBUS project, and it adopted the economic submodule of GLOBUS (developed by the author). GLOBUS had been created with the inspiration of Karl Deutsch and under the leadership of Stuart Bremer (1987) at the Wissenschaftszentrum in Berlin. |
|
| |
|
| 186 countries underpin the functioning of IFs and these countries can be displayed separately or as parts of larger groups that users can determine.
| | The third generation produced three editions/major releases of IFs, each accompanied by a book also called International Futures (Hughes 1993, 1996, 1999). The second edition moved to a Visual Basic platform that allowed a much-improved menu-driven interface, running under Windows. The third edition incorporated an early global mapping capability and an initial ability to do cross-sectional and longitudinal data analysis. |
|
| |
|
| ''Below is a visual representation of how different entities are organized into Countries/Regions, Groups or Glists:'' | | '''The fourth generation''' took shape in early 2000. It was heavily influenced by the usage of the model by several important organizations for policy-analysis. First, General Motors commissioned a specialized version of IFs named CoVaTrA (Consumer Values Trends Analysis) with a need for updated and extended demographic modeling and representation of value change. An alliance was established with the World Values Survey, directed by Ronald Inglehart, to create that version. Second, the Strategic Assessments Group of the Central Intelligence Agency commissioned a specialized version named IFs for SAG. The work involved in preparing that greatly extended and enhanced the socio-political representations of the model, both domestic and international. Third, the European Commission sponsored a project named TERRA which has led to a specialized version named IFs for TERRA. The IFs for TERRA work led to enhancements across the model, including improved representation of economic sectors, updated IO matrices and a basic Social Accounting Matrix, GINI and Lorenz curves, and preparing for extended environmental impact representation (drawing upon the Advanced Sustainability Analysis framework of the Finland Futures Research Center). |
|
| |
|
| [[File:Geo 186.png|frame|right|Visual representation of IF's definition of regions/countries/groups/glists]]
| | The fourth generation of IFs also had a heavy emphasis on enhancing usability. Ideas from Robert Pestel in the TERRA project led to the creation of a new tree-structure for scenario creation and management. Ideas from Ronald Inglehart led to the development of the Guided Use structure and a somewhat more game-like character within that structure. Inglehart also helped to arrange funding to support the programming of Guided Use through the European Union Center of the University of Michigan. |
|
| |
|
| ''*Note: In older versions of IFs, Regions were used as intermediaries between Countries and Groups. In the future, they, or some similarly named unit, will be a sub-unit of Countries. Regions, acting as a sub-unit of Countries, are currently not a feature of IFs. See the image located at the bottom of this Help topic.'' | | '''The fifth generation''' of IFs (from 2004-2009) focused on improving the model, its usability, and transparency. Model improvements included clearer and more extensive representations of the agent classes and their points of leverage, stemming from the desire to make the modeling system a more valuable scenario-testing and policy analysis tool. The further elaboration of the social accounting matrix, structure, the development of education and health sub-models, and the substantial redesign of an economic production function with endogenous multifactor productivity were all outcomes of this version. |
|
| |
|
| When using IFs, there are many occasions where the user is asked whether or not they would like to display their results as a product of single countries, or larger groups. This is typically a toggle switch that moves between Country/Region and Groups, however, it might be a three-way-toggle that includes Country/Region, Group and Glist.
| | Efforts to enhance the model's usability included the addition of a number of specialized displays, such as those for seeing the social accounting matrices, to display progress towards the Millennium Development Goals, to explore poverty at different income levels, and to represent the educational attainment of population cohorts. Mapping and data analysis tools were also strengthened. The ability to drill down into select countries to explore futures at the state or province-level was also added. Packaged Displays and Flex Packaged Displays were introduced that allowed for the creation of very specific lists of countries/regions, groups or G-lists. Greater transparency came from adding the ability for users to access the flow charts, equations, and code underlying the model. |
|
| |
|
| Countries/Regions are currently the smallest geographical unit that users can represent. The ability to split countries down into smaller regions, or states, is under development. There are 186 different countries/regions that users can display.
| | The fifth version was the first version of this software to be placed online due to the help of the National Intelligence Council (http://www.ifs.du.edu). New scenarios were created for UNEP (focusing on environmental change) and Pardee (focusing on poverty). Finally, one of the largest changes made was incorporating 182 countries into the Base-Case scenario used by IFs. Previous versions of IFs used broader regions to forecast global trends. This change also did away with the Student and Professional versions. |
|
| |
|
| Groups are variably organized geographically or by memberships in international institutions/regimes. You can find out who is represented in each group and add or delete members by exploring the [[Extended_Features#Manage_Groups/Regions|Managing Regionalization]] function.
| | '''The sixth generation''' of IFs began in 2010 and revolved around the development of the Patterns of Potential Human Progress (PPHP) series. The [https://korbel.du.edu/pardee/content/patterns-potential-human-progress PPHP] volumes, with their focus on major human development systems, spurred the further enhancement of the model’s major subsystems, especially population, economic (especially poverty representation), education, health, infrastructure, and governance. The supporting documentation required for the PPHP series also gave rise to efforts to create the most detailed documentation of the model to date. The sixth generation greatly strengthened the web-based version. |
|
| |
|
| Glists merge both Groups and Countries/Regions. These lists are mostly geographically bound. In the future, the Glist distinction will become more important as some users may want to place, for example, both the Indian state of Kerala in a Glist with Sri Lanka and Nepal.
| | '''The seventh generation''' officially began in 2014. This generation emerged after the PPHP volumes and with the advent of a variety of new projects, including wider support for provincial and state breakdowns, new means of forecasting diplomatic and power interactions, and enhanced representations in many of the IFs modules. Central to the institute's efforts this version also had continuous improvements in the existing elements of the model and usability. |
|
| |
|
| Users may also want to [[Extended_Features#Change_Grouping/Regionalization|create]] their own groups or [[Extended_Features#Identify_Groups_or_Country/Region_Members|explore]] what countries are members of what groups.
| | '''The current (eighth) generation''' is primarily distinguished by a transition in the underlying coding language, shifting from Visual Basic 6 to Visual Basic .NET. This shift has facilitated the integration of both online and standalone user interfaces, streamlining the process of implementing interface modifications. Moreover, the adoption of this new underlying language and user interface has empowered developers to leverage a broader range of third-party applications and dynamic visualization tools, while aligning with Microsoft-supported languages. |
|
| |
|
| = <span style="font-size:xx-large;">IFs Time Horizon</span> = | | = <span style="font-size:xx-large;">Geographic Representation of the World</span> = |
|
| |
|
| '''Future Forecasts.''' IFs begins computation with data from 2000 and can dynamically calculate values for all variables annually through 2100.
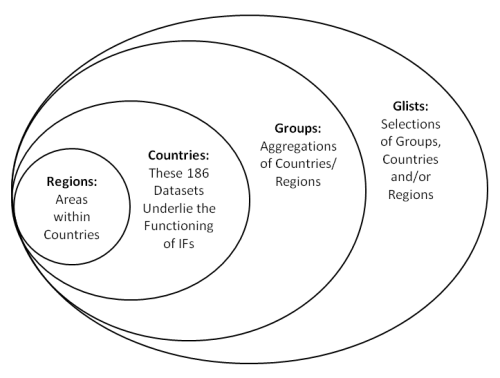
| | 188 countries underpin the functioning of IFs and these countries can be displayed separately or as parts of larger groups that users can determine. |
|
| |
|
| '''Historical Analysis and "Forecasts."''' IFs also includes an extensive and growing historical data base starting in 1960. The data basis allows analysis of relationships among variables across countries and across time. | | ''Below is a visual representation of how different entities are organized into Countries/Regions, Groups or Geography-lists (Sometimes referred to as Gglists):'' |
|
| |
|
| == <span style="font-size:x-large;">Instructional Use</span> ==
| | [[File:Geo 186.png|frame|right|Visual representation of regions, countries, groups, and geography-lists in IFs]] |
|
| |
|
| The standard modes for using IFs in a classroom are:
| | ''*Note: In older versions of IFs, Regions were used as intermediaries between Countries and Groups. In the future, they, or some similarly named unit, will be a sub-unit of Countries. Regions, acting as a sub-unit of Countries, are currently not a feature of IFs. See the image located at the bottom of this Help topic.'' |
| | |
| 1. Assigning class members to an issue area or topic. Consider identifying specific questions for them to address.
| |
| | |
| 2. Assigning class members to a country/geographic region. Again, specificity helps.
| |
| | |
| Most often, students will work independently or in groups on projects and share information after completing them. It is possible, however, to have students work interactively, by assigning them topics or regions, letting them begin work, and then have the interacting groups (or individuals) create a collective model run with the changes that each group proposes by topic or region. That process, although more difficult to organize, allows the class as whole to investigate the interaction of their topics or regions (and to share learning about model use).
| |
| | |
| There is a [http://portfolio.du.edu/bhughes web site] available in support of the educational use of IFs. You will find syllabi at that site. There are several [[Introduction_to_IFs#Publications_on_IFs|publications]] on IFs, including a book structured specifically for educational use.
| |
| | |
| Donald Borock has described his classroom use of IFs in print. Borock, Donald. 1996. "Using Computer Assisted Instruction to Enhance the Understanding of Policymaking," Advances in Social Science and Computers 4, 103-127.
| |
| | |
| = <span style="font-size:xx-large;">Acknowledgements</span> =
| |
| | |
| The author gratefully recognizes critical contributions in the forms of:
| |
| | |
| :1. Testing and suggestions for development of IFs in one or more of multiple generations. By Donald Borock, Richard Chadwick, William Dixon, Dale Rothman, Phil Schrodt, Douglas Stuart, Donald Sylvan, Jonathan Wilkenfeld, and Ronald Inglehart.
| |
| | |
| :2. Computer assistance across many releases. By Michael Niemann, Terrance Peet-Lukes, Douglas McClure, Mohammod Irfan, and Jose Solorzano.
| |
| | |
| :3. Data gathering and general assistance. By James Chung, Padma Padula, Shannon Brady, David Horan, Michael Ferrier, Kay Drucker, Warren Christopher, and Anwar Hossain.
| |
| | |
| :4. Long-term encouragement and support. By Harold Guetzkow, Karl Deutsch, Richard Chadwick, Gerald Barney, and Ronald Inglehart.
| |
| | |
| :5. Association in related world modeling projects and projects building upon IFs. By Mihajlo Mesarovic, Aldo Barsotti, Juan Huerta, John Richardson, Thomas Shook, Patricia Strauch, and other members of the World Integrated Model (WIM) team. By Stuart Bremer, Peter Brecke, Thomas Cusack, Wolf Dieter-Eberwein, Brian Pollins, and Dale Smith of the GLOBUS modeling project. By Evan Hillebrand, Paul Herman, and others of the IFs for SAG project. By Rob Lempert and Steve Bankes at RAND, Santa Monica. By Robert Pestel, Jonathan Cave, Ronald Inglehart, Sergei Parinov, Pentti Malaska, and many others in the IFs for TERRA project.
| |
| | |
| :6. Financial assistance (without responsibility for the form of the evolving product). By the National Science Foundation, the Cleveland Foundation, the Exxon Education Foundation, the Kettering Family Foundation, the Pacific Cultural Foundation, the United States Institute of Peace, General Motors, the Strategic Assessments Group of the Central Intelligence Agency, the European Commission (Information Society Technology) Programme, the European Union Center of the University of Michigan, the National Intelligence Council (for web conversion), and Frederick S. Pardee.
| |
| | |
| = <span style="font-size:xx-large;">Feedback</span> =
| |
| | |
| Feedback on how to improve IFs is always appreciated, especially if you find something that is not working. Compliments are also accepted. Please contact. To send the IFs team an e-mail, click on [mailto:pardee.center@du.edu Pardee Center] in stand-alone versions or on the web.
| |
| | |
| = <span style="font-size:xx-large;">Support for IFs Use</span> =
| |
| | |
| == <span style="font-size:x-large;">Publications on IFs</span> ==
| |
| | |
| To obtain additional information about IFs and its use, consult:
| |
| | |
| Barry B. Hughes and Evan E. Hillebrand, '''Exploring and Shaping International Futures.''' Boulder, CO: Paradigm Publishers, 2006. Specifically, see chapter 4.
| |
| | |
| Barry B. Hughes, '''International Futures: Choices in the Face of Uncertainty,''' 3rd ed. Boulder, CO: Westview Press, 1999. This volume is built around IFs and contains detailed suggestions for its use. Version 3.17 of IFs, which runs under Windows 95, is distributed with the third edition of the book. The second edition contained a version for Windows 3.1, and the first edition ran under DOS. Chapter 4 of the 2nd edition of IFs included Flow Charts of Worldviews , reproduced now in this Help system.
| |
| | |
| Barry B. Hughes, '''Continuity and Change in World Politics,''' 4th ed. Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice Hall, 2000. IFs can also usefully supplement this textbook on global politics.
| |
| | |
| Barry B. Hughes, "The International Futures (IFs) Modeling Project. 1999. '''Simulation and Gaming''' 30, No. 3 (September): 304-326.
| |
| | |
| == <span style="font-size:x-large;">IFs Bibliography</span> ==
| |
| | |
| Alcamo, Joseph, Rik Leemans and Eric Kreileman, eds. 1998. ''Global Change Scenarios of the 21st Century: Results from the IMAGE 2.1 Model''. The Netherlands: Pergamon.
| |
| | |
| Alcamo, Joseph. 1994. ''IMAGE 2.0: Integrated Modeling of Global Climate Change''. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
| |
| | |
| Alexandratos, Nikos, ed. 1995. ''World Agriculture: Towards 2010'' (An FAO Study). New York: FAO and John Wiley and Sons.
| |
| | |
| Allen, R. G. D. 1968. ''Macro-Economic Theory: A Mathematical Treatment''. New York: St. Martin's Press.
| |
| | |
| Avery, Dennis. 1995. "Saving the Planet with Pesticides," in ''The True State of the Planet'', ed. Ronald Bailey. New York: The Free Press, pp. 50-82.
| |
| | |
| Bailey, Ronald, ed. 1995. ''The True State of the Planet''. New York: The Free Press.
| |
| | |
| Barbieri, Kathleen. 1996. "Economic Interdependence: A Path to Peace or a Source of Interstate Conflict?" ''Journal of Peace Research'' 33: 29-50.
| |
| | |
| Barker, T.S. and A.W.A. Peterson, eds. 1987. ''The Cambridge Multisectoral Dynamic Model of the British Economy''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
| |
| | |
| Barney, Gerald O., W. Brian Kreutzer, and Martha J. Garrett, eds. 1991. ''Managing a Nation'', 2nd ed. Boulder: Westview Press.
| |
| | |
| Barro, Robert J. 1997. ''Determinants of Economic Growth: A Cross-Country Empirical Study''. Cambridge, Mass: MIT Press.
| |
| | |
| Barro, Robert J. and Xavier Sala-i-Martin. 1999. ''Economic Growth''. Cambridge, Mass: MIT Press.
| |
| | |
| Bennett, D. Scott, and Allan Stam. 2003. ''The Behavioral Origins of War: Cumulation and Limits to Knowledge in Understanding International Conflict''. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press
| |
| | |
| Birg, Herwig. 1995. ''World Population Projections for the 21st Century''. Frankfurt: Campus Verlag.
| |
| | |
| Borock, Donald M. 1996. "Using Computer Assisted Instruction to Enhance the Understanding of Policymaking," ''Advances in Social Science and Computers'' 4, 103-127.
| |
| | |
| Bos, Eduard, My T. Vu, Ernest Massiah, and Rodolfo A. Bulatao. 1994. ''World Population Projections 1994-95 Edition'' [editions are biannual] Baltimore: Johns Hopkins Press.
| |
| | |
| Boulding, Elise and Kenneth E. Boulding. 1995. ''The Future: Images and Processes''. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
| |
| | |
| Brecke, Peter. 1993. "Integrated Global Models that Run on Personal Computers," ''Simulation''60 (2).
| |
| | |
| Bremer, Stuart A. 1977. ''Simulated Worlds: A Computer Model of National Decision-Making''. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
| |
| | |
| Bremer, Stuart A., ed. 1987. ''The GLOBUS Model: Computer Simulation of World-wide Political and Economic Developments''. Boulder, CO: Westview.
| |
| | |
| Bremer, Stuart A. and Walter Gruhn. 1988. ''Micro GLOBUS: A Computer Model of Long-Term Global Political and Economic Processes''. Berlin: edition sigma.
| |
| | |
| Bremer, Stuart A. and Barry B. Hughes. 1990. ''Disarmament and Development: A Design for the Future?'' Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice-Hall.
| |
| | |
| Brockmeier, Martina and Channing Arndt (presentor). 2002. Social Accounting Matrices. Powerpoint presentation on GTAP and SAMs (June 21). Found on the web.
| |
| | |
| Brown, Lester R. 1981. ''Building a Sustainable Society''. New York: W.W. Norton.
| |
| | |
| Brown, Lester R. 1988. "Analyzing the Demographic Trap," in ''State of the World 1987'', eds. Lester R. Brown and others. New York: W.W. Norton, pp. 20-37.
| |
| | |
| Brown, Lester R. 1995. ''Who Will Feed China?'' New York: W.W. Norton.
| |
| | |
| Brown, Lester R. 1996. ''Tough Choices: Facing the Challenge of Food Scarcity''. New York: W.W. Norton.
| |
| | |
| Brown, Lester R., et al. 1996 ''State of the World 1996''. New York: W.W. Norton.
| |
| | |
| Brown, Lester R., Nicholas Lenssen, and Hal Kane. 1995. ''Vital Signs'' 1995. New York: W.W. Norton.
| |
| | |
| Brown, Lester R., Christopher Flavin, and Hal Kane. 1996. ''Vital Signs'' 1996. New York: W.W. Norton.
| |
| | |
| Burkhardt, Helmut. 1995. "Priorities for a Sustainable Civilization," unpublished conference paper. Department of Physics, Ryerson Polytechnic University, Toronto, Canada.
| |
| | |
| Bussolo, Maurizio, Mohamed Chemingui and David O’Connor. 2002. A Multi-Region Social Accounting Matrix (1995) and Regional Environmental General Equilibrium Model for India (REGEMI). Paris: OECD Development Centre (February). Available at [http://www.oecd.org/dev/technics www.oecd.org/dev/technics].
| |
| | |
| British Petroleum Company. 1995. ''BP Statistical Review of World Energy''. London: British Petroleum Company.
| |
| | |
| Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). 1991. ''Handbook of Economic Statistics, 1991''. Washington, D.C.: Central Intelligence Agency.
| |
| | |
| Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). 1994.'' The World Factbook 1994''. Washington, D.C.: Central Intelligence Agency.
| |
| | |
| Chang, Sheldon S. L. 1961. ''Synthesis of Optimum Control Systems''. New York: McGraw-Hill.
| |
| | |
| Chenery, Hollis and Moises Syrquin. 1975. ''Patterns of Development 1950-1970''. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
| |
| | |
| Cipolla, Carlo M. 1962. ''The Economic History of World Population''. Baltimore: Penguin.
| |
| | |
| Cook, Earl. 1976. ''Man, Energy, Society''. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman.
| |
| | |
| Committee on the Strategic Assessment of the U.S. Department of Energy’s Coal Program. 1995. ''Coal: Energy for the Future''. Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press.
| |
| | |
| Council on Environmental Quality (CEQ). 1981. ''The Global 2000 Report to the President''. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office.
| |
| | |
| Council on Environmental Quality (CEQ). 1981b. ''Environmental Trends''. Washington, D.C. (July).
| |
| | |
| Council on Environmental Quality (CEQ). 1991. ''21st Annual Report''. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office.
| |
| | |
| Crescenzi, Mark J.C. and Andrew J. Enterline. 2001. "Time Remembered: A Dynamic Model of Interstate Interaction," ''International Studies Quarterly'' 45, no. 3 (September): 409-431.
| |
| | |
| Crosson, Pierre, and Jock R. Anderson. 1992. ''Resources and Global Food Prospects''. Washington, D.C.: The World Bank. World Bank Technical Paper Number 184.
| |
| | |
| Cusack, Thomas R. and Richard J. Stoll. 1990. ''Exploring Realpolitik: Probing International Relations with Computer Simulatio''n. Boulder: Lynne Rienner Publishers.
| |
| | |
| Dargay, Joyce and Dermot Gately. 1999. "Income’s Effect on Car and Vehicle Ownership, Worldwide: 1960-2015," ''Transportation Research Part A'' 33: 101-138.
| |
| | |
| Dall, P., Kaspar, F. and Alcamo, J. 1998. "Modeling World-wide Water Availability and Water Use Under the Influence of Climate Change," ''Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Climate and Water'', July 17-20, Espoo, Finland.
| |
| | |
| Dimaranan, Betina V. and Robert A. McDougall, eds. 2002. ''Global Trade, Assistance, and Production: The GTAP 5 Data Base''. Center for Global Trade Analysis, Purdue University. Available at [http://www.gtap.agecon.purdue.edu/databases/v5/v5_doco.asp http://www.gtap.agecon.purdue.edu/databases/v5/v5_doco.asp].
| |
| | |
| Dowlatabadi, H., and Morgan, M.G. 1993. "A Model Framework for Integrated Studies of the Climate Problem," ''Energy Policy'' (March): 209-221.
| |
| | |
| Duchin, Faye. 1998. ''Structural Economics: Measuring Change in Technology, Lifestyles, and the Environment''. Washington, D.C.: Island Press.
| |
| | |
| Edwards, Stephen R. 1995. "Conserving Biodiversity," in'' The True State of the Planet'', ed. Ronald Bailey. New York: The Free Press, pp. 212-265.
| |
| | |
| Edmonds, J., and Reilly, J.M. 1985. ''Global Energy: Assessing the Future''. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
| |
| | |
| Edmonds, J., Pitcher, H. Rosenberg, N., and Wigley, T. "Design for the Global Change Assessment Model." ''Integrative Assessment of Mitigation, Impacts and Adaptation to Climate Change''. Laxenburg, Austria.
| |
| | |
| Ehrlich, Paul R. and Anne H. Ehrlich. 1972. ''Population, Resources, Environment''. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman.
| |
| | |
| Eicher, Carl. 1982. "Facing up to Africa's Food Crisis," ''Foreign Affairs'' 61, no. 1 (Fall): 151-74.
| |
| | |
| Eberstadt, Nicholas. 1995. "Population, Food, and Income," in'' The True State of the Planet'', ed. Ronald Bailey. New York: The Free Press, pp. 8-47.
| |
| | |
| Esty, Daniel C., Jack A. Goldstone, Ted Robert Gurr, Barbara Harff, Marc Levy, Geoffrey D. Dabelko, Pamela T. Surko, and Alan N. Unger. 1998. State Failure Task Force Report: Phase II Findings. Volume provided courtesy of Ted Robert Gurr.
| |
| | |
| Flavin, Christopher. 1996. "Facing Up to the Risks of Climate Change," in Lester R. Brown and others, eds., State of the World 1996 (New York: W.W. Norton), pp. 21-39.
| |
| | |
| Forrester, Jay W. 1968. ''Principles of Systems''. Cambridge, Mass: Wright-Allen Press.
| |
| | |
| Gilpin, Robert. 1981. ''War and Change in World Politics''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
| |
| | |
| Globerman, Steven. 2000 (May). Linkages Between Technological Change and Productivity Growth. Industry Canada Research Publications Program: Occasional Paper 23.
| |
| | |
| Grant, Lindsey. 1982. ''The Cornucopian Fallacies''. Washington, D.C.: Environmental Fund.
| |
| | |
| Griffith, Rachel, Stephen Redding, and John Van Reenen. 2000. ''Mapping the Two Faces of R&D: Productivity Growth in a Panel of OECD Industries''. Institute for Fiscal Studies (January)
| |
| | |
| Gwartney, James and Robert Lawson with Dexter Samida. 2000. ''Economic Freedom of the World: 2000 Annual Report''. Vancouver, B.C.: the Fraser Institute.
| |
| | |
| Hammond, Allen. 1998. ''Which World? Scenarios for the 21st Century''. Washington, D.C.: Island Press.
| |
| | |
| Harff, Barbara, with Ted Robert Gurr and Alan Unger. 1999. Preconditions of Genocide and Politicide: 1955-1998. Paper prepared for the State Failure Task Force and provided courtesy of Barbara Harff and Ted Gurr.
| |
| | |
| Henderson, Hazel. 1996. "Changing Paradigms and Indicators: Implementing Equitable, Sustainable and Participatory Development," in Jo Marie Griesgraber and Bernhard G. Gunter, ''Development: New Paradigms and Principles for the 21st Century''. East Haven, CT: Pluto Press, pp. 103-136.
| |
| | |
| Herrera, Amilcar O., et al. 1976.'' Catastrophe or New Society? A Latin American World Model''. Ottawa: International Development Research Centre.
| |
| | |
| Hoekstra, A.Y. 1998. ''Perspectives on Water: An Integrated Model-Based Exploration of the Future''. Utrecht, the Netherlands: International Books.
| |
| | |
| Hughes, Barry B. 1980. ''World Modeling''. Lexington, Mass: Lexington Books.
| |
| | |
| Hughes, Barry B. 1982. ''International Futures Simulation: User's Manual''. Iowa City: CONDUIT, University of Iowa.
| |
| | |
| Hughes, Barry B. 1985a. ''International Futures Simulation''. Iowa City: CONDUIT, University of Iowa.
| |
| | |
| Hughes, Barry B. 1985b. "World Models: The Bases of Difference," ''International Studies Quarterly'' 29, 77-101.
| |
| | |
| Hughes, Barry B. 1985c. ''World Futures: A Critical Analysis of Alternatives''. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
| |
| | |
| Hughes, Barry B. 1987. "Domestic Economic Processes," in Stuart A. Bremer, ed., ''The Globus Model: Computer Simulation of Worldwide Political Economic Development'' (Frankfurt and Boulder: Campus and Westview), pp. 39-158.
| |
| | |
| Hughes, Barry B. 1988. "International Futures: History and Status," ''Social Science Microcomputer Review'' 6, 43-48.
| |
| | |
| Hughes, Barry B. 1999. "The International Futures (IFs) Modeling Project.'' Simulation and Gaming'' Vol 30, No. 3 (September): 304-326.
| |
| | |
| Hughes, Barry B. 1999. ''International Futures'', 3rd edition Boulder: Westview Press, 1999.
| |
| | |
| Hughes, Barry B. 2000. ''Continuity and Change in World Politics''. Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice-Hall, fourth edition.
| |
| | |
| Hughes, Barry B. 2001. "Global Social Transformation: The Sweet Spot, the Steady Slog, and the Systemic Shift," ''Economic Development and Cultural Change'' 49, No. 2 (January): 423-458.
| |
| | |
| Hughes, Barry B. 2002. ''Theats and Opportunities Analysis''. Living document prepared for the Strategic Assessments Group, Office of Transnational Issues, Central Intelligence Agency, August 2002.
| |
| | |
| Hughes, Barry B. and Anwar Hossain. 2003. Long-Term Socio-Economic Modeling: With Universal, Globally-Integrated Social Accounting Matrices (SAMs) in a General Equilibrium Model Structure. IFs Project Living Document, University of Denver.
| |
| | |
| Huth, Paul. 1996. ''Standing Your Ground: Territorial Disputes and International Conflict''. Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan Press.
| |
| | |
| Inglehart, Ronald. 1997. ''Modernization and Postmodernization: Cultural, Economic, and Political Change in 43 Societies''. Ewing, NJ: Princeton University Press.
| |
| | |
| International Energy Agency (IEA). 1995. ''Oil, Gas, and Coal Supply Outlook''. Paris: International Energy Agency.
| |
| | |
| International Energy Agency (IEA). 1996. ''World Energy Outlook''. Paris: International Energy Agency.
| |
| | |
| International Energy Agency (IEA). 1996b. ''The Strategic Value of Fossil Fuels: Challenges and Responses''. Paris: International Energy Agency.
| |
| | |
| International Monetary Fund (IMF). 1995. ''International Financial Statistics''. Washington, D.C.: International Monetary Fund.
| |
| | |
| International Monetary Fund (IMF). 1995. ''World Economic Outlook''. Washington, D.C.: International Monetary Fund.
| |
| | |
| Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). 1995. Several volumes by various working groups. Published by Cambridge University Press.
| |
| | |
| Jansen, Karel and Rob Vos, eds. 1997. ''External Finance and Adjustment: Failure and Success in the Developing World''. London: Macmillan Press Ltd.
| |
| | |
| Janssen, Marco. 1998. ''Modeling Global Change: The Art of Integrated Assessment Modelling''. Cheltenham, UK: Edward Elgar.
| |
| | |
| Janssen, Marco. 1996. ''Meeting Targets: Tools to Support Integrated Modelling of Global Change''. Den Haag: CIP-Gegevens Koninklijke Bibliotheek.
| |
| | |
| Jansson, Kurt, Michael Harris, Angela Penrose. 1987. ''The Ethiopian Famine''. London: Zed Books Ltd.
| |
| | |
| Jeffreys, Kent. 1995. "Rescuing the Oceans," in'' The True State of the Planet'', ed. Ronald Bailey. New York: The Free Press, pp. 296-338.
| |
| | |
| Jones, Daniel M., Stuart A. Bremer, and J. David Singer. 1996. "Militarized Interstate Disputes, 1816-1992: Rationale, Coding Rules, and Empirical Patterns," ''Conflict Management and Peace Science'' XV, No. 2: 163-215.
| |
| | |
| Khan, Haider A. 1998. ''Technology, Development and Democracy''. Northhampton, Mass: Edward Elgar Publishing Co.
| |
| | |
| Kahn, Herman, William Brown, and Leon Martel. 1976. ''The Next 200 Years''. New York: William Morrow.
| |
| | |
| Kalymon, Basil A. 1975. "Economic Incentives in OPEC Oil Pricing Policy."'' Journal of Development Economics'' 2: 337-362.
| |
| | |
| Kaplan, Robert. 1994. "The Coming Anarchy," ''The Atlantic Monthly'' 273 (February): .
| |
| | |
| Kaufmann, Daniel, Aart Kraay and Pablo Zoido-Lobaton. 1999a. "Aggregating Governance Indicators". World Bank Policy Research Department Working Paper No. 2195.
| |
| | |
| Kaufmann, Daniel, Aart Kraay and Pablo Zoido-Lobaton. 1999b. "Governance Matters". World Bank Policy Research Department Working Paper No. 2196.
| |
| | |
| Keepin, B. and B. Wynne. 1984. "Technical Analysis of the IIASA Energy Scenarios," ''Nature''312: 691-695.
| |
| | |
| Kehoe, Timothy J. 1996. Social Accounting Matrices and Applied General Equilibrium Models. Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis, Working Paper 563.
| |
| | |
| Kennedy, Paul. 1993. ''Preparing for the Twenty-First Century''. New York: Random House.
| |
| | |
| Klein, Lawrence R. and Fu-chen Lo, eds. 1995. ''Modeling Global Change''. Tokyo: United Nations University Press.
| |
| | |
| Kornai, J. 1971. ''Anti-Equilibrium''. Amsterdam: North Holland.
| |
| | |
| Kwasnicki, Witold and Halina Kwasnicka. 1996. "Long-Term Diffusion Factors of Technological Development: An Evolutionary Model and Case Study," ''Technological Forecasting and Social Change'' 52 (May): 31-57.
| |
| | |
| Leontief, Wassily, Anne Carter and Peter Petri. 1977. ''The Future of the World Economy''. New York: Oxford University Press.
| |
| | |
| Levis, Alexander H., and Elizabeth R. Ducot. 1976. "AGRIMOD: A Simulation Model for the Analysis of U.S. Food Policies." Paper delivered at Conference on Systems Analysis of Grain Reserves, Joint Annual Meeting of GRSA and TIMS, Philadelphia, Pa., March 31-April 2.
| |
| | |
| Levis, Alexander, H., et al. 1977. Energy in Agriculture: On Modeling Inputs in AGRIMOD. Final Report to U.S. Department of Energy. Palo Alto: Systems Control, Inc., August, available through NTIS.
| |
| | |
| Lichbach, Mark Irving. 1989. "An Evaluation of ‘Does Economic Inequality Breed Political Conflict?," ''World Politics'', Vol 41 , No. 4 (July 1989): 431-470.
| |
| | |
| Liverman, Dianne. 1983. ''The Use of Global Simulation Models in Assessing Climate Impacts on the World Food System''. Dissertation, University of California, Los Angeles.
| |
| | |
| Londregan, John B. and Keith T. Poole. 1996. "Does High Income Promote Democrary?", ''World Politics'' 49, no. 1 (October): 1-30.
| |
| | |
| MacKenzie, James J. 1996. "Oil as a Finite Resource: When is Global Production Likely to Peak?" Paper of the World Resources Institute. Washington, D.C.: WRI.
| |
| | |
| Maddison, Angus. 1995. ''Monitoring the World Economy 1820-1992''. Paris: OECD.
| |
| | |
| Malthus, Thomas. 1798. ''An Essay on the Principle of Population as It Affects the Future Improvement of Society''. London (reprinted many times).
| |
| | |
| Mansfield, Edward D. 1994. ''Power, Trade, and War''. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
| |
| | |
| Marchetti, Cesare, Perrin S. Meyer, and Jesse H. Ausubel. 1996. "Human Population Dynamics Revisited with the Logistic Model: How Much Can be Modeled and Predicted?," ''Technological Forecasting and Social Change'' 52 (May): 1-30.
| |
| | |
| Martens, Pim and Jan Rotmans, eds. 1999. ''Climate Change: An Integrated Perspective''. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
| |
| | |
| Martens, W.J.M. 1997. "Health Impacts of Climate Change and Ozone Depletion: An Eco-Epidemiological Approach," Maastricht, the Netherlands: Maastricht University.
| |
| | |
| Mason, Andrew. 1997. "The Role of Population Change in the Asian Economic Miracle," Honolulu, Hawaii: East-West Center, AsiaPacific Issues, No. 33 (October), 8 pages.
| |
| | |
| McMahon, Walter W. 1997. ''Education and Development: Measuring the Social Benefits''. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
| |
| | |
| Meadows, Donnela H., Dennis L. Meadows, Jorgen Randers, and William K. Behrens, III. 1972. ''Limits to Growth''. New York: Universe Books.
| |
| | |
| Meadows, Donnela H., Dennis L. Meadows, and Jorgen Randers. 1992. ''Beyond the Limits''. Post Mills, Vermont: Chelsea Green Publishing Company.
| |
| | |
| Meadows, Dennis L. et al. 1974. ''Dynamics of Growth in a Finite World''. Cambridge, Mass: Wright-Allen Press.
| |
| | |
| Mesarovic, Mihajlo D. and Eduard Pestel. 1974. ''Mankind at the Turning Point''. New York: E.P. Dutton & Co.
| |
| | |
| Mishkin, Eli. And Ludwig Braun, ed. 1961. ''Adaptive Control Systems''. New York: McGraw-Hill.
| |
| | |
| Moore, Will H., Ronny Lindstrom, and Valerie O’Regan. 1996. "Land Reform, Political Violence and the Economic Inequality-Political Conflict Nexus: A Longitudinal Analysis," ''International Interactions'' 21, No. 4: 335-363.
| |
| | |
| Mori, Shunsuke and Masato Takahaashi, 1997. An Integrated Assessment Model for the Evaluation of New Energy Technologies and Food Production, accepted by ''International Journal of Global Energy Issues''.
| |
| | |
| Naill, Roger F. 1977. ''Managing the Energy Transition''. Vols. 1 and 2. Cambridge, Mass: Ballinger Publishing Co.
| |
| | |
| Nordhaus, William D. 1992. "The DICE Model: Background and Structure of a Dynamic Integrated Climate Economy," New Haven: Yale University.
| |
| | |
| Nordhaus, William D. 1979. ''The Efficient Use of Energy Resources''. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.
| |
| | |
| Oneal, John R. and Bruce M. Russett. 1997. The Classical Liberals were Right: Democracy, Interdependence, and Conflict, 1950-1985. ''International Studies Quarterly'' 41, no. 2 (June): 267-294.
| |
| | |
| Pan, Xiaoming. 2000 (January). "Social and Ecological Accounting Matrix: an Empirical Study for China," paper submitted for the Thirteenth International Conference on Input-Output Techniques, Macerata, Italy, August 21-25, 2000.
| |
| | |
| Pesaran, M. Hashem and G. C. Harcourt. 1999. Life and Work of John Richard Nicholas Stone.
| |
| | |
| Pirages, Dennis. 1989. ''Global Technopolitics''. Pacific Grove, Calif: Brooks/Cole Publishing.
| |
| | |
| Prinn, R. H.J., A. Sokolov, C. Wand, X. Xiao, Z. Yang, R. Eckhaus, P. Stone, D. Ellerman, J Melilo, J. Fitzmaurice, D. Kicklighter, and Y. Liu. 1996. "Integrated Global System Model for Climate Policy Analysis: Model Framework and Sensitivity Analysis." Cambridge, Mass: Global Change Center, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
| |
| | |
| Przeworski, Adam and Fernando Limongi. 1997. "Modernization: Theories and Facts," ''World Politics'' 49, no. 2 (January): 155-183.
| |
| | |
| Population Reference Bureau. 1996. World Population Data Sheet 1996. Washington, D.C.: Population Reference Bureau.
| |
| | |
| Postel, Sandra. 1996. ''Dividing the Waters: Food Security, Ecosystem Health, and the New Politics of Scarcity''. Worldwatch Paper 132. Washington, D.C.: Worldwatch Institute, September.
| |
| | |
| Pyatt, G. and J.I. Round, eds. 1985. ''Social Accounting Matrices: A Basis for Planning''. Washington, D.C.: The World Bank.
| |
| | |
| Raskin, P., T. Banuri, G. Gallopín, P. Gutman, A. Hammond, R. Kates, and R. Swart. 2001. Great Transition: ''The Promise and Lure of the Times Ahead''. Forthcoming.
| |
| | |
| Ray, James Lee. 1990. ''Global Politics'', 4th edition. Boston: Houghton Mifflin.
| |
| | |
| Ray, James Lee. 1995. ''Democracy and International Conflict''. Columbia: University of South Carolina Press.
| |
| | |
| Ray, James Lee and J. David Singer. 1973. " Measuring the Concentration of Power in the International System,"'' Sociological Methods and Research'' 1, no. 4: 403-436. Reprinted in ''Measuring the Correlates of War'', edited by J. David Singer and Paul Diehl. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press, 1990.
| |
| | |
| Rayner. S. 1992. "Cultural Theory and Risk Analysis," ''Social Theory of Risk'', ed. G. D. Preagor. Westport, USA.
| |
| | |
| Repetto, Robert and Duncan Austin. 1997. ''The Costs of Climate Protection''. Washington, D.C.: World Resources Institute.
| |
| | |
| Richardson, Lewis Fry. 1960. ''Arms and Insecurity''. Chicago: Quadrangle Books.
| |
| | |
| Richardson, Lewis F. 1960. ''Arms and Insecurity''. Pittsburgh: Boxwood Press.
| |
| | |
| Romer, Paul M. 1994. "The Origins of Endogenous Growth," ''Journal of Economic Perspectives''Vol 8, No. 1 (Winter): 3-22.
| |
| | |
| Root T. and Stephen Schneider. 1995. "Ecology and Climate: Research Strategies and Implications," Science 269 (52): 334-341.
| |
| | |
| Rosegrant, Mark W., Mercedita Agcaoili-Sombilla, and Nicostrato D. Perez. 1995. "Global Food Projections to 2020: Implications for Investment." Washington, D.C.: International Food Policy Research Institute. Food, Agriculture, and the Environment Discussion Paper 5.
| |
| | |
| Rotmans, Jan. 1999. Integrated Assessment Models: Uncertainty, Quality and Use. Maastricht, the Netherlands: Maastricht University, International Centre for Integrative Studies (ICIS), Working Paper 199-E005.
| |
| | |
| Rotmans, Jan and Burt de Vries, eds. 1997. ''Perspectives on Global Change: The Targets Approach''. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
| |
| | |
| Rotmans, Jan and M.B.A. van Asselt. 1996. "Integrated Assessment: A Growing Child on its Way to Maturity," ''Climatic Change'' 34 (3-4): 327-336.
| |
| | |
| Rotmans, Jan. 1990. ''IMAGE: An Integrated Model to Assess the Greenhouse Effect''. Dordrecht, the Netherlands: Kluwer Academics.
| |
| | |
| Saaty, Thomas L. 1996. The Analytic Network Process: Decision Making with Dependence and Feedback. Pittsburgh: RWS Publications.
| |
| | |
| Schafer, Andreas and David G. Victor. 1997. The Future Mobility of the World Population. Massachusetts Institute of Technology and International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis, Discussion Paper 97-6-4 (revision 2, September).
| |
| | |
| Scheer, Sara J. and Satya Yadav. 1996. "Land Degradation in the Developing World: Implications for Food, Agriculture, and the Environment to 2020." Washington, D.C.: International Food Policy Research Institute. Food, Agriculture, and the Environment Discussion Paper 14.
| |
| | |
| Schneider, Stephen. 1997. "Integrated Assessment Modeling of Climate Change: Transparent Rational Tool for Policy Making or Opaque Screen Hiding Value-Laden Assumptions?" ''Environmental Modelling and Assessment'' 2(4): 229-250.
| |
| | |
| Schwartz, Peter. 1996.'' The Art of the Long View.'' New York: Doubleday.
| |
| | |
| Sedjo, Roger A. 1995. "Forests: Conflicting Signals," in ''The True State of the Planet'', ed. Ronald Bailey. New York: The Free Press, pp. 178-209.
| |
| | |
| Shane, Harold G. and Gary A. Sojka. 1990. "John Elfreth Watkins, Jr.: Forgotten Genius of Forecasting," in Edward Cornish, ed.,'' The 1990s and Beyond''. Bethesda, Maryland: World Future Society, pp. 150-155.
| |
| | |
| Shaw, Timothy W. and Clement E. Adibe. 1995-96. "Africa and Global Developments in the Twenty-First Century," International Journal 51 (Winter): 1-26.
| |
| | |
| Siegmann, Heinrich. 1985. ''Recent Developments in World Modeling''. Berlin: Science Center.
| |
| | |
| Simon, Julian. 1981. ''The Ultimate Resource''. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
| |
| | |
| Singer, J. David, Stuart Bremer, and John Stuckey. 1972. "Capability Distribution, Uncertainty, and Major Power Wars, 1820-1965." In Bruce Russett, ed., ''Peace, War, and Numbers.'' Beverly Hills: Sage.
| |
| | |
| Sivard, Ruth Leger. 1993. ''World Military and Social Expenditures 1993.'' Washington, D.C. 20007: World Priorities, Box 25140.
| |
| | |
| Solow, Robert M. 1956. "A Contribution to the Theory of Economic Growth," ''Quarterly Journal of Economics'' 70, 1 (February): 65-94.
| |
| | |
| Stanford University. 1978. ''Stanford Pilot Energy/Economic Model''. Stanford: Department of Research, Interim Report, Vol. 1.
| |
| | |
| Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI). 1994. ''SIPRI Yearbook''. New York: Oxford University Press.
| |
| | |
| Stone, Richard. 1986. "The Accounts of Society,"'' Journal of Applied Econometrics'' 1, no. 1 (January): 5-28.
| |
| | |
| Strategic Assessments Group (SAG), Office of Transnational Issues, Directorate of Intelligence. 2001 (February). The Global Economy in the Long Term. OTI IR 2001-013.
| |
| | |
| Systems Analysis Research Unit (SARU). 1977. ''SARUM 76 Global Modeling Project''. Departments of the Environment and Transport, 2 Marsham Street, London, 3WIP 3EB.
| |
| | |
| Tammen, Ronald L, Jacek Kugler, Douglas Lemke, Allan C. Stam III, Carole Alsharabati, Mark Andrew Abdollahian, Brian Efird, and A.F.K. Organski. 2000. Power Transitions: Strategies for the 21st Century. New York: Chatham House Publishers.
| |
| | |
| Taylor, Lance. 1975. "Theoretical Foundations and Technical Implications." in Charles Blitzer, Peter Clark and Lance Taylor, eds., ''Economy-Wide Models and Development Planning.'' Oxford: Oxford University Press.
| |
| | |
| Taylor, Lance. 1979. ''Macro Models for Developing Countries''. New York: McGraw-Hill.
| |
| | |
| Thirlwall, A. P. 1977. ''Growth and Development''. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
| |
| | |
| Thompson, M. 1997. Cultural Theory and Integrated Assessment. ''Environmental Modelling and Assessment'' 2(3): 139-150.
| |
| | |
| Thompson, M., R. Ellis and A. Wildavsky. 1990. ''Cultural Theory''. Boulder, Co: Westview Press.
| |
| | |
| Thorbecke, Erik. 2001. "The Social Accounting Matrix: Deterministic or Stochastic Concept?", paper prepared for a conference in honor of Graham Pyatt's retirement, at the Institute of Social Studies, The Hague, Netherlands (November 29 and 30). Available at [http://people.cornell.edu/pages/et17/etpapers.html http://people.cornell.edu/pages/et17/etpapers.html].
| |
| | |
| United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs. 1956. ''Methods of Population Projections by Sex and Age''. New York: United Nations, ST/SOA Series A.
| |
| | |
| United Nations (UN). 1992. ''Long-Range World Population Projections. Two Centuries of Population Growth: 1950-2150''. New York: United Nations.
| |
| | |
| United Nations (UN). 1993. ''World Population Prospects - the 1992 Revision''. New York: United Nations.
| |
| | |
| United Nations Development Program (UNDP). 1995. ''Human Development Report''. New York: Oxford University Press.
| |
| | |
| United Nations Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO). 1992. ''Production Yearbook.'' Rome: FAO.
| |
| | |
| United Nations Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO). 1995.'' World Agriculture: Towards 2010.'' Rome: FAO.
| |
| | |
| United Nations Population Division. 1999. The World at Six Billion New York: UN.
| |
| | |
| United Nations Population Division. 2000. Replacement Migration: Is it a Solution to Declining and Ageing Populations? New York: UN.
| |
| | |
| United States Arms Control and Disarmament Agency (ACDA). 1995. ''World Military Expenditures and Arms Transfers 1995''. Washington, D.C.: Arms Control and Disarmament Agency.
| |
| | |
| United States Bureau of the Census. 1991. ''World Population Profile: 1991''. Report WP/91 Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office.
| |
| | |
| Walters, Robert S. and David H. Blake. 1992. ''The Politics of Global Economic Relations'', 4th edition. Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice-Hall.
| |
| | |
| Waltz, Kenneth N. 1959. Man, the State, and War: A Theoretical Analysis. New York: Columbia University Press.
| |
| | |
| Watkins, John Elfreth, Jr. 1990. "What May Happen in the Next Hundred Years," in Edward Cornish, ed., ''The 1990s and Beyond.'' Bethesda, Maryland: World Future Society, pp. 150-155.
| |
| | |
| Wildavsky, Aaron, and Ellen Tenenbaum. 1981. ''The Politics of Mistrust''. Beverly Hills: Sage Publications.
| |
| | |
| World Bank. 1991b. ''World Tables 1991''. New York: Johns Hopkins University Press.
| |
| | |
| World Bank. 1995 ''World Development Report 1995''. New York: Oxford University Press.
| |
| | |
| World Energy Council (WEC) Commission. 1993. ''Energy for Tomorrow’s World.'' New York: St. Martin’s Press.
| |
| | |
| World Resources Institute (WRI). 1994. ''World Resources 1994-95.'' New York: Oxford University Press.
| |
| | |
| Wortman, Sterling and Ralph W. Cummings, Jr. 1978.'' To Feed This World''. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press.
| |
| | |
| Zinnes, Dina A. and John W. Gillespie, eds. 1976. ''Mathematical Models in International Relations'' (New York: Preaeger).
| |
| | |
| == <span style="font-size:x-large;">Health Bibliography</span> ==
| |
| | |
| Adams 1987. [http://www.geog.ucl.ac.uk/~jadams/PDFs/smeed's%20law.pdf "Smeed's Law: some further thoughts."] ''Traffic Engineering and Control'' (Feb) 70-73.
| |
| | |
| Alsan, Marcella, David E. Bloom, and David Canning. 2006. “The Effects of Population Health on Foreign Direct Investment Inflows to Low- and Middle-Income Countries,” ''World Development'' 34(4): 613-630.
| |
| | |
| Anand, Sudhir and Martin Ravallion. 1993. “Human development in poor countries: on the role of private incomes and public services,” ''Journal of Economic Perspectives'' 7(1): 133–150.
| |
| | |
| Ashraf, Quamrul H., Ashley Lester, and David N. Weil. 2008. “When Does Improving Health Raise GDP?” NBER Working Paper No. 14449. National Bureau of Economic Research, Cambridge, MA.
| |
| | |
| Bidani, Benu and Martin Ravallion. 1997. “Decomposing social indicators using distributional data.” ''Journal of Econometrics'' 77: 125–139.
| |
| | |
| Bloom, David E., and David Canning. 2004. “Global Demographic Change: Dimensions and Economic Significance.” NBER Working Paper No. 10817. National Bureau of Economic Research, Cambridge, MA.
| |
| | |
| Blössner, Monika, and Mercedes de Onis. 2005. ''Malnutrition: quantifying the health impact at national and local levels.'' Geneva, World Health Organization. (WHO Environmental Burden of Disease Series, No. 12).
| |
| | |
| Dargay, Gately, and Sommer 2007. “Vehicle Ownership and Income Growth, Worldwide: 1960-2030”. Joyce Dargay, Dermot Gately and Martin Sommer, January 2007.
| |
| | |
| Deaton, Angus, and Christina Paxson. 2000 (May). “Growth and Savings Among Individuals and Households.” ''The Review of Economics and Statistics'' 82(2): 212-225.
| |
| | |
| Desai, Manish A., Sumi Mehta, and Kirk R. Smith. 2004. “Indoor smoke from solid fuels: Assessing the environmental burden of disease.”WHOEnvironmental Burden of Disease Series No. 4''. ''Annette Pruss-Üstun, Diamid Campbell-Lendrum, Carlos Corvalán, and Alistair Woodward, series eds. World Health Organization, Geneva.
| |
| | |
| Ezzati, Majid and Alan D. Lopez. 2004. “Smoking and oral tobacco use.” In Majid Ezzati, Alan D. Lopez, Anthony Rodgers, and Cristopher J.L. Murray, eds., ''Comparative Quantification of Health Risks: Global and Regional Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risk Factors''. Geneva: World Health Organization, 883-957. Retrieved 4 Feb 2009, from [http://www.who.int/publications/cra/chapters/volume1/part4/en/index.html http://www.who.int/publications/cra/chapters/volume1/part4/en/index.html].
| |
| | |
| Ezzati, Majid, Alan D. Lopez, Anthony Rodgers, Christopher J.L. Murray, eds. 2004. ''Comparative Quantification of Health Risks: Global and Regional Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risk Factors''. Geneva: World Health Organization.
| |
| | |
| Fernández-Villaverde, Jesús, and Dirk Kruegger. 2004 (September 14). “Consumption over the Life Cycle: Facts from Consumer Expenditure Survey Data,” unpublished manuscript, University of Pennsylvania and University of Frankfort. [http://www.dklevine.com/archive/refs4506439000000000304.pdf http://www.dklevine.com/archive/refs4506439000000000304.pdf]
| |
| | |
| Fernández-Villaverde, Jesús, and Dirk Kruegger. 2005 (December 19). “Consumption over the Life Cycle: How Important are Consumer Durables?,” unpublished manuscript, University of Pennsylvania and Goethe University. [http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=8466457 http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=8466457]
| |
| | |
| Gakidou, Emmanuela, Shefali Oza, Cecilia Vidal Fuertes, Amy Y. Li, Diana K. Lee, Angelica Sousa, Margaret C. Hogan, Stephen Vander Hoorn, and Majid Ezzati. 2007.” Improving Child Survival Through Environmental and Nutritional Interventions: The Importance of Targeting Interventions Toward the Poor.” ''Journal of the American Medical Association'' 298(16): 1876-1887.
| |
| | |
| Hughes, Barry B. and Hillebrand, Evan E. 2006. “Exploring and shaping International Futures”. Boulder, CO: Paradigm Publishers.
| |
| | |
| Hughes, Barry B., Randall Kuhn, Cecilia Peterson, Dale Rothman, and Jose Solorzano. 2011. ''Improving Global Health: Patterns of Potential Human Progress, Volume 3''. Paradigm Publishing and Oxford India.
| |
| | |
| Hughes, Barry B. 2005. “Productivity in IFs.” Pardee Center for International Futures Working Paper, University of Denver, Denver, CO. [http://www.ifs.du.edu/documents/reports.aspx http://www.ifs.du.edu/documents/reports.aspx].
| |
| | |
| James, W. Philip T., Rachel Jackson-Leach , Cliona Ni Mhurchu, Eleni Kalamara, Maryam Shayeghi, Neville J. Rigby, Chizuru Nishida, and Anthony Rodgers. 2004. “Overweight and obesity (high body mass index).” In Majid Ezzati, Alan D. Lopez, Anthony Rodgers and Christopher J.L. Murray, eds., ''Comparative Quantification of Health Risks: Global and Regional Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risk Factors.'' Geneva: World Health Organization, 959-1108.
| |
| | |
| Jamison, Dean T., Jia Wang, Kenneth Hill, and Juan-Luis Londono. 1996. “Income, Mortality and Fertility in Latin America: Country-Level Performance, 1960 - 90.” ''Analisis Economico''11(2): 219-261.
| |
| | |
| Kelly, Christopher, Nora Pashayan, Sreetharan Munisamy, and Joshn W. Powles. 2009. “Mortality attributable to excess adiposity in England and Wales in 2003 and 2015: explorations with a spreadsheet implementation of the Comparative Risk Assessment mentodology.” ''Population Health Metrics'' 7(11): 1-7.
| |
| | |
| Lopez, Alan D., Neil E. Collishaw, and Tapani Piha. 1994. “A descriptive model of the cigarette epidemic in developed countries.” ''Tobacco Control'' 3(3): 242-247.
| |
| | |
| Mathers, Colin D., and Dejan Loncar. 2005. "Updated Projections of Global Mortality and Burden of Disease, 2002-2030: Data Sources, Methods and Results." Evidence and Information for Policy Working Paper. World Health Organization, Geneva.
| |
| | |
| Mathers, Colin D., and Dejan Loncar. 2006. "Projections of Global Mortality and Burden of Disease from 2002 to 2030." ''PLoS Medicine'' 3(11): e442, 2011-2030. Retrieved 13 March 2009. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0030442.
| |
| | |
| Mathers, Colin D., and Dejan Loncar. 2006b. “New projections of global mortality and burden of disease from 2002 to 2030.” Protocol S1. Technical Appendix to Mathers and Loncar 2006.
| |
| | |
| Mathers, Colin D., and Dejan Loncar. 2006c. “Results of Regressions of Age–Sex-Specific Mortality for Detailed Causes on the Respective Cause Cluster Based on the Full Country Panel Dataset, 1950–2002.” Technical Appendix to Mathers and Loncar 2006.
| |
| | |
| Nixon, John, and Philippe Ulmann. 2006. “The Relationship Between Health Care Expenditure and Health Outcomes: Evidence and caveats for a Causal Link.” ''European Journal of Health Economics'' 7: 7-18.
| |
| | |
| Peto, Richard, Jillian Boreham, Alan D. Lopez, Michael Thun, and Clark Heath, Jr. 1992. “Mortality from Tobacco in Developed Countries: Indirect Estimation from National Vital Statistics.” ''Lancet ''339(8804): 1268–1278. doi:10.1016/0140- 6736(92)91600-D.
| |
| | |
| Ploeg, Martine, Katja K. H. Aben, and Lambertus A. Kiemeney. 2009. “The Present and Future Burden of Urinary Bladder Cancer in the World.” ''World Journal of Urology'' 27(3): 289-293. doi:[http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00345-009-0383-3 10.1007/s00345-009-0383-3 ].
| |
| | |
| Shibuya, Kenji, Mie Inoue, and Alan D. Lopez. 2005. “Statistical Modeling and Projections of Lung Cancer Mortality in 4 Industrialized Countries.” ''International Journal of Cancer'' 117(3): 476-485. doi:[http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijc.21078 10.1002/ijc.21078 ].
| |
| | |
| Smeed, RJ 1949. "Some statistical aspects of road safety research". [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Royal_Statistical_Society ''Royal Statistical Society''], Journal (A) CXII (Part I, series 4). 1-24.
| |
| | |
| Smith, Lisa C. and Lawrence Haddad. 2000. “Explaining Child Malnutrition in Developing Countries: A Cross-Sectional Analysis.” Washington, D.C.: International Food Policy Research Institute.
| |
| | |
| Soares, Rodrigo R. 2007. “On the Determinants of Mortality Reductions in the Developing World.” ''Population and Development Review ''33(2): 247-287.
| |
| | |
| United Nations Population Division. 2003. '' '' ''World Population Prospects: The 2002 Revision, Highlight.'' New York: United Nations. Department of Economics and Social Affairs.
| |
| | |
| United Nations Population Division. 2009. '' '' ''World Population Prospects: The 2008 Revision, Highlights.'' New York: United Nations. Department of Economics and Social Affairs.
| |
| | |
| Wagstaff, Adam. 2002. “Inequalities in Health in Developing Countries: Swimming Against the Tide?” Unpublished Manuscript
| |
| | |
| == <span style="font-size:x-large;">Infrastructure Bibliography</span> ==
| |
| | |
| Agénor, Pierre-Richard, Mustapha Kamel Nabli, and Tarik M. Yousef. 2007. “Public Infrastructure and Private Investment in the Middle East and North Africa.” In Mustapha Kamel Nabli, ed.,. Breaking the Barriers to Higher Economic Growth: Better Governance and Deeper Reforms in the Middle East and North Africa. Washington, DC: World Bank Publications, 399–422.
| |
| | |
| Asian Development Bank, Japan Bank for International Cooperation, and World Bank. 2005. ''Connecting East Asia: A New Framework for Infrastructure''. Tokyo: Asian Development Bank, Japan Bank for International Cooperation, and World Bank. [http://siteresources.worldbank.org/INTEASTASIAPACIFIC/Resources/Connecting-East-Asia.pdf http://siteresources.worldbank.org/INTEASTASIAPACIFIC/Resources/Connecting-East-Asia.pdf].
| |
| | |
| Bhattacharyay, Biswa Nath. 2010. “Estimating Demand for Infrastructure in Energy, Transport, Telecommunications, Water and Sanitation in Asia and the Pacific: 2010-2020”. Working Paper no. 248. Asian Development Bank Institute, Tokyo. [http://www.adbi.org/working-paper/2010/09/09/4062.infrastructure.demand.asia.pacific/ http://www.adbi.org/working-paper/2010/09/09/4062.infrastructure.demand.asia.pacific/].
| |
| | |
| Bruinsma, Jelle. 2011. “The Resources Outlook: By How Much Do Land, Water and Crop Yields Need to Increase by 2050?” In Piero Conforti, ed.,. ''Looking Ahead in World Food and Agriculture: Perspectives to 2050''. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), 233–275. [http://www.fao.org/docrep/014/i2280e/i2280e.pdf http://www.fao.org/docrep/014/i2280e/i2280e.pdf].
| |
| | |
| Calderón, César, and Luis Servén. 2010a. “Infrastructure and Economic Development in Sub-Saharan Africa.” ''Journal of African Economies'' 19(Supplement 1): i13–i87. doi:10.1093/jae/ejp022. [http://jae.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/19/suppl_1/i13 http://jae.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/19/suppl_1/i13].
| |
| | |
| Calderón, César, and Luis Servén. 2010b. “Infrastructure in Latin America”. World Bank Policy Research Working Paper. Report Number 5317. World Bank, Washington, DC.
| |
| | |
| Canning, David. 1998. “A Database of World Stocks of Infrastructure, 1950-1995.” ''The World Bank Economic Review'' 12(3): 529–548.
| |
| | |
| Canning, David, and Mansour Farahani. 2007. “A Database of World Stocks of Infrastructure: Update 1950-2005”. Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, MA. [http://www.hsph.harvard.edu/faculty/david-canning/data-sets/ http://www.hsph.harvard.edu/faculty/david-canning/data-sets/].
| |
| | |
| Cavallo, Eduardo Alfredo, and Christian Daude. 2008. “Public Investment in Developing Countries: A Blessing or a Curse?” RES Working Paper #4597. Inter-American Development Bank (IADB) - Research Department, OECD, Washington, DC.
| |
| | |
| Chatterton, Isabe, and Olga S. Puerto. 2006. ''Estimation of Infrastructure Investment Needs in the South Asia Region: Executive Summary''. Washington, DC: World Bank. [http://siteresources.worldbank.org/INTSARREGTOPTRANSPORT/Resources/Inf_Investment_Needs_IC_version4.pdf http://siteresources.worldbank.org/INTSARREGTOPTRANSPORT/Resources/Inf_Investment_Needs_IC_version4.pdf].
| |
| | |
| Congressional Budget Office. 2010. ''Public Spending on Transportation and Water Infrastructure''. Washington, DC: Congressional Budget Office. [http://www.cbo.gov/publication/21902 http://www.cbo.gov/publication/21902].
| |
| | |
| Estache, Antonio, and Ana Goicoechea. 2005. “A Research Database on Infrastructure Economic Performance”. Policy Research Working Paper no. 3643. World Bank, Washington, DC. [http://www-wds.worldbank.org/servlet/WDSContentServer/WDSP/IB/2005/06/16/000016406_20050616100502/Rendered/PDF/wps3643.pdf http://www-wds.worldbank.org/servlet/WDSContentServer/WDSP/IB/2005/06/16/000016406_20050616100502/Rendered/PDF/wps3643.pdf].
| |
| | |
| Ezzati, Majid, Alan D. Lopez, Anthony Rodgers, and Christopher J. L. Murray, eds. 2004. ''Comparative Quantification of Health Risks: Global and Regional Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risk Factors''. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization (WHO).
| |
| | |
| Fay, Marianne. 2001. “Financing the Future: Infrastructure Needs in Latin America, 2000-05”. Policy Research Working Paper no. 2545. World Bank, Washington, DC. [http://elibrary.worldbank.org/docserver/download/2545.pdf?expires=1375200693&id=id&accname=guest&checksum=DB7E5FB146EE28C93511B5ADAB2FD3CB http://elibrary.worldbank.org/docserver/download/2545.pdf?expires=1375200693&id=id&accname=guest&checksum=DB7E5FB146EE28C93511B5ADAB2FD3CB].
| |
| | |
| Fay, Marianne, and Tito Yepes. 2003. “Investing in Infrastructure: What Is Needed from 2000 to 2010?” Policy Research Working Paper no. 3102. World Bank, Washington, DC. RePEc. [http://ideas.repec.org/p/wbk/wbrwps/3102.html http://ideas.repec.org/p/wbk/wbrwps/3102.html].
| |
| | |
| Hughes, Barry B. 2007. “Forecasting Global Economic Growth with Endogenous Multifactor Productivity: The International Futures (IFs) Approach”. Pardee Center for International Futures Working Paper, University of Denver. Denver, CO. [http://www.ifs.du.edu/documents/reports.aspx www.ifs.du.edu/documents/reports.aspx].
| |
| | |
| Hughes, Barry B., Devin Joshi, Jonathan Moyer, Timothy Sisk and José Roberto Solórzano. 2014. Strengthening Governance Globally. vol. 5, Patterns of Potential Human Progress series. Boulder, CO, and New Delhi, India: Paradigm Publishers and Oxford University Press.
| |
| | |
| Hughes, Gordon, Paul Chinowsky, and Ken Strzepek. 2009. “The Costs of Adapting to Climate Change for Infrastructure”. Economics of Adaptation to Climate Change Discussion Paper no. 2. World Bank, Washington, DC.
| |
| | |
| International Transport Forum, and Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). 2011. “Trends in Transport Infrastructure Investment 1995-2009”. Paris.
| |
| | |
| Kohli, Harpaul Alberto, and Phillip Basil. 2011. “Requirements for Infrastructure Investment in Latin America Under Alternate Growth Scenarios.” ''Global Journal of Emerging Market Economies'' 3(1): 59 –110. doi:10.1177/097491011000300103. [http://eme.sagepub.com/content/3/1/59.abstract http://eme.sagepub.com/content/3/1/59.abstract].
| |
| | |
| Kim, M. Julie, and Rita Nangia. 2010. “Infrastructure Development in India and China—A Comparative Analysis.” In William Ascher and Corinne Krupp, eds.,. ''Physical Infrastructure Development: Balancing The Growth, Equity, and Environmental Imperatives''. New York, NY: Palgrave Macmillan, 97–140.
| |
| | |
| Lora, Eduardo A. 2007. ''Public Investment in Infrastructure in Latin America: Is Debt the Culprit?'' Inter-American Development Bank Working Paper. Washington, DC: Inter-American Development Bank (IADB) - Research Department.
| |
| | |
| Nelson, Gerald C., Mark W. Rosegrant, Amanda Palazzo, Ian Gray, Christina Ingersoll, Richard Robertson, Simla Tokgoz, Tingju Zhu, Timothy B. Sulser, Claudia Ringler, Siwa Msangi, and Liangzhi You. 2010. ''Food Security, Farming, and Climate Change to 2050: Scenarios, Results, Policy Options''. Washington, DC: International Food Policy Research Institute. [http://www.ifpri.org/publication/food-security-farming-and-climate-change-2050 http://www.ifpri.org/publication/food-security-farming-and-climate-change-2050].
| |
| | |
| Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. 2006. ''Infrastructure to 2030 Volume 1: Telecom, Land Transport, Water and Electricity''. Infrastructure to 2030. Paris: Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development.
| |
|
| |
|
| Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. 2009. ''Going for Growth: Economic Policy Reforms''. Paris: Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD).
| | When using IFs, there are many occasions where the user must decide whether or not they would like to display their results as a product of single countries, or larger groups. This is typically a toggle switch that moves between Country/Region and Groups; however, it might be a three-way-toggle that includes Country/Region, Group and Geography-List. |
|
| |
|
| Qiang, Christine Zhen-Wei, Carlo M. Rossotto, and Kaoru Kimura. 2009. “Economic Impacts of Broadband.” In World Bank, ed.,. ''2009 Information and Communications for Development: Extending Reach and Increasing Impact''. Washington, DC: World Bank, 35–50.
| | Countries/Regions are currently the smallest geographical unit that users can represent. The ability to split countries down into smaller regions, or states, is under development. There are 188 different countries/regions that users can display. |
|
| |
|
| Rothman, Dale S. Mohammod T. Irfan, Eli Margolese-Malin, Barry B. Hughes, Jonathan Moyer, and Janet Dickson. 2013. ''Building Global Infrastructure. ''vol. 4, Patterns of Potential Human Progress series. Boulder, CO, and New Delhi, India: Paradigm Publishers and Oxford University Press. Stambrook, David. 2006. “Key Factors Driving the Future Demand for Surface Transport Infrastructure and Services.” In Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), ed.,. ''Infrastructure to 2030 Volume 1: Telecom, Land Transport, Water and Electricity''. Infrastructure to 2030. Paris: Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), 185–239.
| | Groups are variably organized geographically, by income, or by memberships in international institutions/regimes. |
|
| |
|
| World Health Organization, and UNICEF. 2013. ''Progress on Sanitation and Drinking-Water - 2013 Update''. Geneva: World Health Organization.
| | Geography-lists ''(Sometimes referred to as Gglists)'' merge both Groups and Countries/Regions. These lists are mostly geographically bound. In the future, the Geography-list distinction will become more important as some users may want to place, for example, both the Indian state of Kerala in a Geography-list with Sri Lanka and Nepal. |
|
| |
|
| Yepes, Tito. 2008. “Investment Needs for Infrastructure in Developing Countries 2008-15”. Draft. World Bank, Washington, DC.
| | Users may also want to explore what countries are members of what groups which can be done through the Identify Groups or Country/Region Members option under [[Extended Features]] tab in the Main Menu. Users that want to [[Extended Features#Change%20Grouping/Regionalization|create]] their own groups can do so through the Edit Groups or Country/Region Members option also under the [[Extended Features]] tab. |
|
| |
|
| Yepes, Tito. 2005. ''Expenditure on Infrastructure in East Asia Region, 2006–2010''. East Asia Pacific Infrastructure Flagship Study. Manila: Asian Development Bank (ADB), Japan Bank for International Cooperation (JBIC), World Bank.
| | <span style="font-size:xx-large;">IFs Time Horizon</span> |
|
| |
|
| You, Liangzhi, Claudia Ringler, Ulrike Wood-Sichra, Richard Robertson, Stanley Wood, Tingju Zhu, Gerald Nelson, Zhe Guo, and Yan Sun. 2011. “What Is the Irrigation Potential for Africa? A Combined Biophysical and Socioeconomic Approach.” ''Food Policy'' 36(6): 770–782. doi:10.1016/j.foodpol.2011.09.001. [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S030691921100114X http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S030691921100114X].
| | '''Future Forecasts.''' IFs begins computation with data from 2020 and can dynamically calculate values for all variables annually through 2100. |
|
| |
|
| == [[Development_Mode_Features|Development Mode Features]] ==
| | '''Historical Analysis and "Forecasts."''' IFs also includes an extensive and growing historical database starting in 1960. The database allows analysis of relationships among variables across countries and across time. |